MENU
The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project: Providing access to classic scientific papers and other scholarly materials, since 1993. More About: ESP | OUR CONTENT | THIS WEBSITE | WHAT'S NEW | WHAT'S HOT
Comparative Timelines
The ESP Timeline (one of the site's most popular features) has been completely updated to allow the user to select (using the timeline controls above each column) different topics for the left and right sides of the display.
Select:
New Left Column
New Left Column
Dates
Decade
New Right Column
New Right Column
(no entry for this year)
1420
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1421
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1422
(no entry for this year)
 Painting by Gentile da Fabriano: The Adoration of the Magi is a painting by the Italian painter Gentile da Fabriano. The work, housed in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence, Italy, is considered his finest work, and has been described as "the culminating work of International Gothic painting". The artwork was commissioned by the famous banker Palla Strozzi and incorporates many notable elements. The choice of materials including the vibrant colors, gold leaf, and silver used in the painting creates a brilliant and attractive effect. Techniques such as lighting, depth, and three-dimensionality are prevalent in the work and were novel for the time. The frame, along with the painting, is a work of art in itself, specifically because of the intricate, Gothic, and ornamental architectural designs incorporated into it.
Painting by Gentile da Fabriano: The Adoration of the Magi is a painting by the Italian painter Gentile da Fabriano. The work, housed in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence, Italy, is considered his finest work, and has been described as "the culminating work of International Gothic painting". The artwork was commissioned by the famous banker Palla Strozzi and incorporates many notable elements. The choice of materials including the vibrant colors, gold leaf, and silver used in the painting creates a brilliant and attractive effect. Techniques such as lighting, depth, and three-dimensionality are prevalent in the work and were novel for the time. The frame, along with the painting, is a work of art in itself, specifically because of the intricate, Gothic, and ornamental architectural designs incorporated into it.
1423
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1424
(no entry for this year)
 Sculpture by Lorenzo Ghiberti: The Gates of Paradise. In 1425, Ghiberti, by then widely recognized as the most accomplished sculptor in Florence, received a second commission to design the east doors of the Baptistery, on which he and his workshop toiled for 27 years (1425–1452). The original gates adorned the Baptistery for nearly 500 years until there was an urgent need to protect them from the bombing by the Nazis during World War II. Before they were reinstalled in 1954, gypsum molds were made that were archived for future use. In 1990, the original doors were moved inside the Museo dell’Opera to protect and preserve the doors.
Sculpture by Lorenzo Ghiberti: The Gates of Paradise. In 1425, Ghiberti, by then widely recognized as the most accomplished sculptor in Florence, received a second commission to design the east doors of the Baptistery, on which he and his workshop toiled for 27 years (1425–1452). The original gates adorned the Baptistery for nearly 500 years until there was an urgent need to protect them from the bombing by the Nazis during World War II. Before they were reinstalled in 1954, gypsum molds were made that were archived for future use. In 1990, the original doors were moved inside the Museo dell’Opera to protect and preserve the doors.
1425
(no entry for this year)
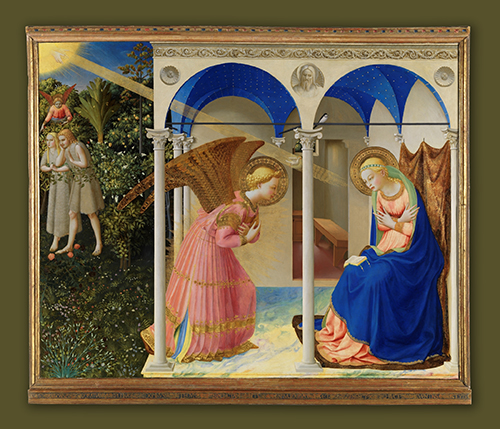 Painting by Fra Angelico: The Prado Annunciation, an altarpiece painted in the 1420s. It is one of Fra Angelico's best-known works. Originally destined for the convent of the observant Dominicans of Fiesole, the painting is currently in the collection of the Museo del Prado in Madrid. It is one of three altarpieces by Fra Angelico representing the Annunciation; the other two being the Cortona Annunciation and the Annunciation of San Giovanni Valdarno. The sequence in which the three works were painted is not certain, but the general art historical consensus places the Prado version first. The work was painted for a side altar in the Convent of San Domenico, Fiesole, where Fra Angelico was a friar. For the same church he also contributed the main altarpiece, showing the Virgin and Child Enthroned with Dominican saints (c. 1425) and the Coronation of the Virgin, now in the Louvre (c. 1424–1435) . The Annunciation remained at San Domenico until 1611 when it was sold to the King of Spain and taken to Madrid, where it became part of the royal collections of the Spanish monarchy before moving to Prado.
Painting by Fra Angelico: The Prado Annunciation, an altarpiece painted in the 1420s. It is one of Fra Angelico's best-known works. Originally destined for the convent of the observant Dominicans of Fiesole, the painting is currently in the collection of the Museo del Prado in Madrid. It is one of three altarpieces by Fra Angelico representing the Annunciation; the other two being the Cortona Annunciation and the Annunciation of San Giovanni Valdarno. The sequence in which the three works were painted is not certain, but the general art historical consensus places the Prado version first. The work was painted for a side altar in the Convent of San Domenico, Fiesole, where Fra Angelico was a friar. For the same church he also contributed the main altarpiece, showing the Virgin and Child Enthroned with Dominican saints (c. 1425) and the Coronation of the Virgin, now in the Louvre (c. 1424–1435) . The Annunciation remained at San Domenico until 1611 when it was sold to the King of Spain and taken to Madrid, where it became part of the royal collections of the Spanish monarchy before moving to Prado.
1426
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1427
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1428
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1429
(no entry for this year)
Work begins in Florence on Brunelleschi's Pazzi chapel, which encapsulates in miniature the new ideals of Renaissance architecture.
1430
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1431
(no entry for this year)
 Painting by Fra Angelico: The Annunciation of San Giovanni Valdarno, a painting in tempera on panel. It is part of a series of Annunciation panels painted by Fra Angelico in the 1430s. The other two are the Annunciation of Cortona and the Annunciation. The Annunciation of San Giovanni Valdarno was looted from Italy during the Second World War by the Germans and returned to the country via the work of Rodolfo Siviero. It is now held at the Museo della Basilica di Santa Maria delle Grazie in San Giovanni Valdarno. The scene is composed in a similar manner to the first panel in the series, the Annunciation of Cortona, with some differences. First of all, the composition is divided into two sections rather than three, with the garden reduced to a glimpse through the arches on the left side. Mary and the angel are placed and clothed like the Annunciation of Cortona, with a greater use of light. The illumination arrives consistently from the left, from the garden, to light drapery and the architecture. Fra Angelico used a vanishing point placed inside the house, rather than outside, which concentrates attention on the spectacle of the Annuciation. Like Masolino da Panicale's Annunciation, the scene's space is divided in two by arches on the first floor. The building has a transitional architecture somewhere between traditional pointed, polyptych medieval design and the squared architecture of the Renaissance. At the center of the arches, there is a medallion with a figure of a prophet, who is looking at Mary and holds in his hand a paper that certifies the truth of his prophecy. Unlike many works of the time from Arezzo, the painting depicts a range of rich colors. The colors vary from the green of the garden, to the rose and gold of the angel's clothes, to the blue and red of Mary, ending with the starry ceiling of the portico and the delicate marble decorations of the walls and floor.
Painting by Fra Angelico: The Annunciation of San Giovanni Valdarno, a painting in tempera on panel. It is part of a series of Annunciation panels painted by Fra Angelico in the 1430s. The other two are the Annunciation of Cortona and the Annunciation. The Annunciation of San Giovanni Valdarno was looted from Italy during the Second World War by the Germans and returned to the country via the work of Rodolfo Siviero. It is now held at the Museo della Basilica di Santa Maria delle Grazie in San Giovanni Valdarno. The scene is composed in a similar manner to the first panel in the series, the Annunciation of Cortona, with some differences. First of all, the composition is divided into two sections rather than three, with the garden reduced to a glimpse through the arches on the left side. Mary and the angel are placed and clothed like the Annunciation of Cortona, with a greater use of light. The illumination arrives consistently from the left, from the garden, to light drapery and the architecture. Fra Angelico used a vanishing point placed inside the house, rather than outside, which concentrates attention on the spectacle of the Annuciation. Like Masolino da Panicale's Annunciation, the scene's space is divided in two by arches on the first floor. The building has a transitional architecture somewhere between traditional pointed, polyptych medieval design and the squared architecture of the Renaissance. At the center of the arches, there is a medallion with a figure of a prophet, who is looking at Mary and holds in his hand a paper that certifies the truth of his prophecy. Unlike many works of the time from Arezzo, the painting depicts a range of rich colors. The colors vary from the green of the garden, to the rose and gold of the angel's clothes, to the blue and red of Mary, ending with the starry ceiling of the portico and the delicate marble decorations of the walls and floor.
 Ghent Alterpiece is completed. This very large and complex 15th-century polyptych altarpiece was begun around the mid-1420s and completed by 1432. The altarpiece is one of the most renowned and important artworks in European history. The panels are organized in two vertical registers, each with double sets of foldable wings containing inner panel paintings (visible when opened) and outer panel paintings (visible when closed).
Ghent Alterpiece is completed. This very large and complex 15th-century polyptych altarpiece was begun around the mid-1420s and completed by 1432. The altarpiece is one of the most renowned and important artworks in European history. The panels are organized in two vertical registers, each with double sets of foldable wings containing inner panel paintings (visible when opened) and outer panel paintings (visible when closed).
Upper register, opened: The scenes represent the heavenly redemption, and includes the central classical Deësis arrangement of God (identified either as Christ the King or God the Father), flanked by the Virgin Mary and John the Baptist. They are flanked in the next panels by angels playing music and, on the far outermost panels, the figures of Adam and Eve.
Lower register, opened: The central panel of the lower register shows a gathering of saints, sinners, clergy, and soldiers attendant at an adoration of the Lamb of God. There are several groupings of figures, overseen by the dove of the Holy Spirit.
Upper register, closed: The archangel Gabriel and the Annunciation, and at the very top are the prophets and sibyls.
Lower register, closed: The four lower panels of the closed altar are divided into two pairs; sculptural grisaille paintings of St John the Baptist and St John the Evangelist, and on the two outer panels, donor portraits of Joost Vijdt and his wife Lysbette Borluut.
1432
(no entry for this year)
 Painting by Domenico di Bartolo: Madonna of Humility, is recorded to be the artist's first-ever commissioned piece of artwork. Renaissance Scholar Bruce Cole refers to Domenico's Madonna of Humility with Angels as "one of the loveliest works of the early Sienese Quattrocento". The composition of the painting is centered with a very volumetrically and triangularly depicted Madonna. Behind her are five angels, who form a semicircle that gives further movement and depth into the painted space. Referring back to several of the Madonna panels by Masaccio that have survived until today, a similarity between them and Domenico's Madonna is that the large figures created dominating geometrical forms that give the overall image a strong sense of sculptural stability and gravity. Art historians also mention that the color palette of the painting is of particular skill and thoughtfulness. The green, pink and blue of the Madonna's robes in contrast with the paleness of the angels' garments and the pale green of the cloth on the infant all come together to display a trait that was peculiar to the Sienese paintings that were produced around the 1400s.
Painting by Domenico di Bartolo: Madonna of Humility, is recorded to be the artist's first-ever commissioned piece of artwork. Renaissance Scholar Bruce Cole refers to Domenico's Madonna of Humility with Angels as "one of the loveliest works of the early Sienese Quattrocento". The composition of the painting is centered with a very volumetrically and triangularly depicted Madonna. Behind her are five angels, who form a semicircle that gives further movement and depth into the painted space. Referring back to several of the Madonna panels by Masaccio that have survived until today, a similarity between them and Domenico's Madonna is that the large figures created dominating geometrical forms that give the overall image a strong sense of sculptural stability and gravity. Art historians also mention that the color palette of the painting is of particular skill and thoughtfulness. The green, pink and blue of the Madonna's robes in contrast with the paleness of the angels' garments and the pale green of the cloth on the infant all come together to display a trait that was peculiar to the Sienese paintings that were produced around the 1400s.
 Painting by Fra Angelico: The Annunciation of Cortona, a panel-painting altarpiece or retable. Once housed in the Church of Gesù of Cortona, it is now held at the Museo Diocesano in Cortona. The Annunciation of Cortona was painted by Fra Angelico in 1433–1434, in tempera on panel, 175 cm × 180 cm. This is one of three Annunciations by Fra Angelico on panel (the other two are in the Prado Museum, and the Museo della Basilica di Santa Maria delle Grazie, in San Giovanni Valdarno. Two others, in fresco, are found in the convent of San Marco, Florence, at the top of the access stairs and the third cell. There are also scenes of the theme combined with Adoration of the Magi at the Museum San Marco, and a diptych in the Galleria Nazionale dell'Umbria.
Painting by Fra Angelico: The Annunciation of Cortona, a panel-painting altarpiece or retable. Once housed in the Church of Gesù of Cortona, it is now held at the Museo Diocesano in Cortona. The Annunciation of Cortona was painted by Fra Angelico in 1433–1434, in tempera on panel, 175 cm × 180 cm. This is one of three Annunciations by Fra Angelico on panel (the other two are in the Prado Museum, and the Museo della Basilica di Santa Maria delle Grazie, in San Giovanni Valdarno. Two others, in fresco, are found in the convent of San Marco, Florence, at the top of the access stairs and the third cell. There are also scenes of the theme combined with Adoration of the Magi at the Museum San Marco, and a diptych in the Galleria Nazionale dell'Umbria.
 Painting by Jan van Eyck: Portrait of a Man (Self Portrait?) The inscription at the top of the panel, Als Ich Can (intended as "as I/Eyck can") was a common autograph for van Eyck, but here is unusually large and prominent. This fact, along with the man's unusually direct and confrontational gaze, have been taken as an indication that the work is a self-portrait. Like all van Eyck's portraits, it shows a sharp and detailed analysis of the subject. The painting is a third life-size with the sitter sitting in three-quarters profile. His stubbled face is heavily lined with the onset of middle age, and his eyes are semi-bloodshot. He looks outwards with a piercing gaze, looking directly at the viewer — possibly being the first portrait in a millennium to do so. His weary facial expression is achieved through a combination of his strong nose, tightly pursed wide mouth and the framing of his face by the headdress. The overall expression is of a man, who one scholar says "see things — himself included — in close-up, but without losing track of the bigger picture."
Painting by Jan van Eyck: Portrait of a Man (Self Portrait?) The inscription at the top of the panel, Als Ich Can (intended as "as I/Eyck can") was a common autograph for van Eyck, but here is unusually large and prominent. This fact, along with the man's unusually direct and confrontational gaze, have been taken as an indication that the work is a self-portrait. Like all van Eyck's portraits, it shows a sharp and detailed analysis of the subject. The painting is a third life-size with the sitter sitting in three-quarters profile. His stubbled face is heavily lined with the onset of middle age, and his eyes are semi-bloodshot. He looks outwards with a piercing gaze, looking directly at the viewer — possibly being the first portrait in a millennium to do so. His weary facial expression is achieved through a combination of his strong nose, tightly pursed wide mouth and the framing of his face by the headdress. The overall expression is of a man, who one scholar says "see things — himself included — in close-up, but without losing track of the bigger picture."
1433
(no entry for this year)
 Painting by Jan van Eyck: Arnolfini Portrait, a full-length double portrait, believed to depict the Italian merchant Giovanni di Nicolao Arnolfini and his wife, presumably in their residence at the Flemish city of Bruges. It is considered one of the most original and complex paintings in Western art, because of its beauty, complex iconography, geometric orthogonal perspective, and expansion of the picture space with the use of a mirror. According to Ernst Gombrich "in its own way it was as new and revolutionary as Donatello's or Masaccio's work in Italy. A simple corner of the real world had suddenly been fixed on to a panel as if by magic... For the first time in history the artist became the perfect eye-witness in the truest sense of the term". The portrait has been considered by Erwin Panofsky and some other art historians as a unique form of marriage contract, recorded as a painting. Signed and dated by van Eyck in 1434, it is, with the Ghent Altarpiece by the same artist and his brother Hubert, the oldest very famous panel painting to have been executed in oils rather than in tempera. The painting was bought by the National Gallery in London in 1842. Van Eyck used the technique of applying several layers of thin translucent glazes to create a painting with an intensity of both tone and color. The glowing colors also help to highlight the realism, and to show the material wealth and opulence of Arnolfini's world. Van Eyck took advantage of the longer drying time of oil paint, compared to tempera, to blend colors by painting wet-in-wet to achieve subtle variations in light and shade to heighten the illusion of three-dimensional forms.
Painting by Jan van Eyck: Arnolfini Portrait, a full-length double portrait, believed to depict the Italian merchant Giovanni di Nicolao Arnolfini and his wife, presumably in their residence at the Flemish city of Bruges. It is considered one of the most original and complex paintings in Western art, because of its beauty, complex iconography, geometric orthogonal perspective, and expansion of the picture space with the use of a mirror. According to Ernst Gombrich "in its own way it was as new and revolutionary as Donatello's or Masaccio's work in Italy. A simple corner of the real world had suddenly been fixed on to a panel as if by magic... For the first time in history the artist became the perfect eye-witness in the truest sense of the term". The portrait has been considered by Erwin Panofsky and some other art historians as a unique form of marriage contract, recorded as a painting. Signed and dated by van Eyck in 1434, it is, with the Ghent Altarpiece by the same artist and his brother Hubert, the oldest very famous panel painting to have been executed in oils rather than in tempera. The painting was bought by the National Gallery in London in 1842. Van Eyck used the technique of applying several layers of thin translucent glazes to create a painting with an intensity of both tone and color. The glowing colors also help to highlight the realism, and to show the material wealth and opulence of Arnolfini's world. Van Eyck took advantage of the longer drying time of oil paint, compared to tempera, to blend colors by painting wet-in-wet to achieve subtle variations in light and shade to heighten the illusion of three-dimensional forms.
1434
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1435
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1436
(no entry for this year)
 Painting by Domenico di Bartolo: Madonna and Child
Painting by Domenico di Bartolo: Madonna and Child
 Painting by Filippo Lippi: Enthroned Madonna and Child,
Painting by Filippo Lippi: Enthroned Madonna and Child,
1437
(no entry for this year)
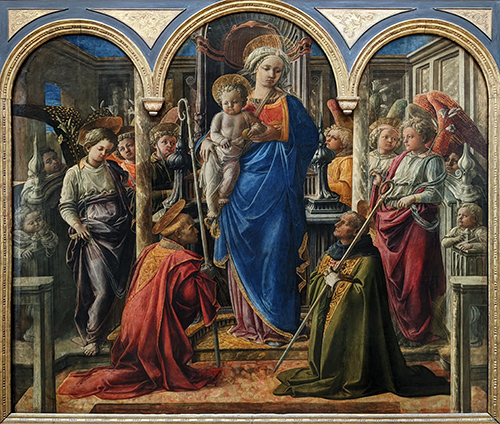 Painting by Filippo Lippi: Barbadori Altarpiece, now in the Louvre Museum in Paris. It may be considered as a very early sacra conversazione. Gherardo di Bartolomeo Barbadori, who died childless in 1429, left his heritage to the Captains of Orsanmichele for the realization, in the church of Santo Spirito, Florence, of a chapel dedicated to Saint Fridianus. The chapel was built in the old sacristy of the church and in 1433 it was decided to place an altarpiece there. The work was commissioned to Filippo Lippi around 1437, and a letter from Piero de' Medici to Domenico Veneziano, dated 1 April 1438, mentions the altarpiece as having not been finished yet. The painting remained in Santo Spirito until 1810, when it was disassembled and brought to France by the Napoleonic troops. After the 1815 restoration it was not given back.
Painting by Filippo Lippi: Barbadori Altarpiece, now in the Louvre Museum in Paris. It may be considered as a very early sacra conversazione. Gherardo di Bartolomeo Barbadori, who died childless in 1429, left his heritage to the Captains of Orsanmichele for the realization, in the church of Santo Spirito, Florence, of a chapel dedicated to Saint Fridianus. The chapel was built in the old sacristy of the church and in 1433 it was decided to place an altarpiece there. The work was commissioned to Filippo Lippi around 1437, and a letter from Piero de' Medici to Domenico Veneziano, dated 1 April 1438, mentions the altarpiece as having not been finished yet. The painting remained in Santo Spirito until 1810, when it was disassembled and brought to France by the Napoleonic troops. After the 1815 restoration it was not given back.
1438
(no entry for this year)
 Painting by Jan van Eyck: Portrait of Margaret van Eyck, one of the latest of van Eyck's surviving paintings, and one of the earliest European artworks to depict a painter's spouse. Completed when Margaret van Eyck was around 34, it was hung until the early 18th century in the Bruges Chapel of the Guild of Painters. Art historians believe it was once a pendant (diptych) panel for Jan's likely self-portrait in the National Gallery, London. Margaret's portrait is in the collection of the Groeningemuseum in Bruges, Belgium.
Painting by Jan van Eyck: Portrait of Margaret van Eyck, one of the latest of van Eyck's surviving paintings, and one of the earliest European artworks to depict a painter's spouse. Completed when Margaret van Eyck was around 34, it was hung until the early 18th century in the Bruges Chapel of the Guild of Painters. Art historians believe it was once a pendant (diptych) panel for Jan's likely self-portrait in the National Gallery, London. Margaret's portrait is in the collection of the Groeningemuseum in Bruges, Belgium.
1439
(no entry for this year)
 Painting by Domenico di Bartolo: Care of the Sick, shows, with impressive detail, the interior layout of the hospital ward. Doctors and nurses are depicted assisting the patients, as well as carrying out other generous deeds. The fresco also depicts in the center foreground the washing of the patient's feet, directly inferring to the well-known image of Christ washing the feet of his disciples. Throughout the whole painting, Domenico vividly brings out the color of the costume and its well-crafted décor. Because of such imitation of a real location, Domenico is said to have followed the works of Vecchietta, where both artists pave the way into a whole new area of descriptive realism to the world of Sienese art. Other painters at the time such as Gentile da Fabriano and Pisanello might have depicted landscapes to be realistic or naturalistic, but they were consistently known to create images that came out of fantasy and creativity. It was therefore new to the art world for both Domenico and Vecchietta to produce images that seem to imitate a specific location. The frescoes by Domenico are also one of the first works done in Sienese art that includes visual clues for its viewers.
Painting by Domenico di Bartolo: Care of the Sick, shows, with impressive detail, the interior layout of the hospital ward. Doctors and nurses are depicted assisting the patients, as well as carrying out other generous deeds. The fresco also depicts in the center foreground the washing of the patient's feet, directly inferring to the well-known image of Christ washing the feet of his disciples. Throughout the whole painting, Domenico vividly brings out the color of the costume and its well-crafted décor. Because of such imitation of a real location, Domenico is said to have followed the works of Vecchietta, where both artists pave the way into a whole new area of descriptive realism to the world of Sienese art. Other painters at the time such as Gentile da Fabriano and Pisanello might have depicted landscapes to be realistic or naturalistic, but they were consistently known to create images that came out of fantasy and creativity. It was therefore new to the art world for both Domenico and Vecchietta to produce images that seem to imitate a specific location. The frescoes by Domenico are also one of the first works done in Sienese art that includes visual clues for its viewers.
1440
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1441
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1442
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1443
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1444
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1446
(no entry for this year)
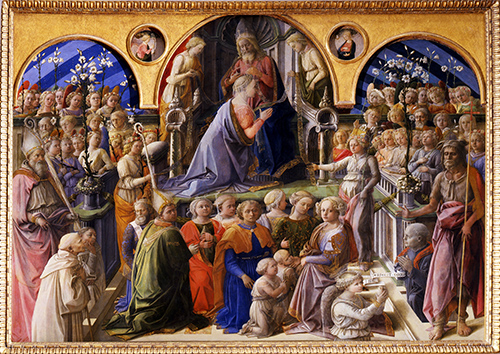 Painting by Filippo Lippi: Coronation of the Virgin, now in the Uffizi, Florence. Francesco Maringhi, procuratore of the church of Sant'Ambrogio, left money after his death in 1441 for a new painting at the high altar of the church. Bills of the payments for the work until 1447 have been preserved. In the late 1430s, brother Filippo Lippi had left the convent of the Carmine convent to open an artist workshop of his own; however, having no money enough to pay assistants and apprentices, he worked alone with two usual collaborators, Fra Carnevale and Fra Diamante, along with an unknown "Piero di Lorenzo dipintore". For the Coronation of the Virgin, however, Lippi had to call in a total of six external painters, who were responsible also for the gilded frame, now lost. Originally the work had a predella, also lost, with the exception of a small panel with a Miracle of Saint Ambrose, now in the Berlin State Museums. The work was immediately admired and was copied by numerous painters. It remained in Sant'Ambrogio until 1810, when it was stolen. Later it was sold to the Galleria dell'Accademia, from which it was transferred to the Galleria degli Uffizi in Florence.
Painting by Filippo Lippi: Coronation of the Virgin, now in the Uffizi, Florence. Francesco Maringhi, procuratore of the church of Sant'Ambrogio, left money after his death in 1441 for a new painting at the high altar of the church. Bills of the payments for the work until 1447 have been preserved. In the late 1430s, brother Filippo Lippi had left the convent of the Carmine convent to open an artist workshop of his own; however, having no money enough to pay assistants and apprentices, he worked alone with two usual collaborators, Fra Carnevale and Fra Diamante, along with an unknown "Piero di Lorenzo dipintore". For the Coronation of the Virgin, however, Lippi had to call in a total of six external painters, who were responsible also for the gilded frame, now lost. Originally the work had a predella, also lost, with the exception of a small panel with a Miracle of Saint Ambrose, now in the Berlin State Museums. The work was immediately admired and was copied by numerous painters. It remained in Sant'Ambrogio until 1810, when it was stolen. Later it was sold to the Galleria dell'Accademia, from which it was transferred to the Galleria degli Uffizi in Florence.
1447
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1448
(no entry for this year)
 Painting by Filippo Lippi: The Annunciation, a tempera on panel painting, dating to c. 1449–1459, in the collection of the National Gallery, London. It is a pendant to Lippi's Seven Saints, also in the National Gallery. The lunettes were commissioned as part of the decoration of the Palazzo Medici in Florence, where they were likely placed above a door or a bed. There is general agreement on Lippi's authorship of the panels, but their dating is less certain; they were produced some time between Lorenzo the Magnificent's birth in 1449 and the completion of the palace's furnishing in 1459. That their patron belonged to the Medici family is testified by the presence of Piero di Cosimo de' Medici's coat of arms (three feathers crossed by a ring with diamond and cartouche) at the base of the small column with a vase which divides the painting in two. The painting depicts the Annunciation of Mary with the archangel Gabriel (left) and Mary (right). God, whose hand can be seen at the lunette's top is blessing Mary through the dove symbolizing the Holy Ghost.
Painting by Filippo Lippi: The Annunciation, a tempera on panel painting, dating to c. 1449–1459, in the collection of the National Gallery, London. It is a pendant to Lippi's Seven Saints, also in the National Gallery. The lunettes were commissioned as part of the decoration of the Palazzo Medici in Florence, where they were likely placed above a door or a bed. There is general agreement on Lippi's authorship of the panels, but their dating is less certain; they were produced some time between Lorenzo the Magnificent's birth in 1449 and the completion of the palace's furnishing in 1459. That their patron belonged to the Medici family is testified by the presence of Piero di Cosimo de' Medici's coat of arms (three feathers crossed by a ring with diamond and cartouche) at the base of the small column with a vase which divides the painting in two. The painting depicts the Annunciation of Mary with the archangel Gabriel (left) and Mary (right). God, whose hand can be seen at the lunette's top is blessing Mary through the dove symbolizing the Holy Ghost.
1449
(no entry for this year)
 Painting by Filippo Lippi: (The Uffizi) Madonna with Child. The date in which it was executed is unknown, but most art historians agree that it was painted during the last part of Lippi's career, between 1450 and 1465. It is one of the few works by Lippi which was not executed with the help of his workshop and was an influential model for later depictions of the Madonna and Child, including those by Sandro Botticelli. The painting is housed in the Uffizi Gallery, Florence, Italy, and is therefore commonly called "The Uffizi Madonna" among art historians.
Painting by Filippo Lippi: (The Uffizi) Madonna with Child. The date in which it was executed is unknown, but most art historians agree that it was painted during the last part of Lippi's career, between 1450 and 1465. It is one of the few works by Lippi which was not executed with the help of his workshop and was an influential model for later depictions of the Madonna and Child, including those by Sandro Botticelli. The painting is housed in the Uffizi Gallery, Florence, Italy, and is therefore commonly called "The Uffizi Madonna" among art historians.
1450
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1451
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1452
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1453
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1454
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1455
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1456
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1457
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1458
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1459
(no entry for this year)
ESP Quick Facts
ESP Origins
In the early 1990's, Robert Robbins was a faculty member at Johns Hopkins, where he directed the informatics core of GDB — the human gene-mapping database of the international human genome project. To share papers with colleagues around the world, he set up a small paper-sharing section on his personal web page. This small project evolved into The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Support
In 1995, Robbins became the VP/IT of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, WA. Soon after arriving in Seattle, Robbins secured funding, through the ELSI component of the US Human Genome Project, to create the original ESP.ORG web site, with the formal goal of providing free, world-wide access to the literature of classical genetics.
ESP Rationale
Although the methods of molecular biology can seem almost magical to the uninitiated, the original techniques of classical genetics are readily appreciated by one and all: cross individuals that differ in some inherited trait, collect all of the progeny, score their attributes, and propose mechanisms to explain the patterns of inheritance observed.
ESP Goal
In reading the early works of classical genetics, one is drawn, almost inexorably, into ever more complex models, until molecular explanations begin to seem both necessary and natural. At that point, the tools for understanding genome research are at hand. Assisting readers reach this point was the original goal of The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Usage
Usage of the site grew rapidly and has remained high. Faculty began to use the site for their assigned readings. Other on-line publishers, ranging from The New York Times to Nature referenced ESP materials in their own publications. Nobel laureates (e.g., Joshua Lederberg) regularly used the site and even wrote to suggest changes and improvements.
ESP Content
When the site began, no journals were making their early content available in digital format. As a result, ESP was obliged to digitize classic literature before it could be made available. For many important papers — such as Mendel's original paper or the first genetic map — ESP had to produce entirely new typeset versions of the works, if they were to be available in a high-quality format.
ESP Help
Early support from the DOE component of the Human Genome Project was critically important for getting the ESP project on a firm foundation. Since that funding ended (nearly 20 years ago), the project has been operated as a purely volunteer effort. Anyone wishing to assist in these efforts should send an email to Robbins.
ESP Plans
With the development of methods for adding typeset side notes to PDF files, the ESP project now plans to add annotated versions of some classical papers to its holdings. We also plan to add new reference and pedagogical material. We have already started providing regularly updated, comprehensive bibliographies to the ESP.ORG site.
ESP Picks from Around the Web (updated 06 MAR 2017 )
Old Science

Weird Science

Treating Disease with Fecal Transplantation
Fossils of miniature humans (hobbits) discovered in Indonesia

Dinosaur tail, complete with feathers, found preserved in amber.
Astronomy

Mysterious fast radio burst (FRB) detected in the distant universe.