MENU
The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project: Providing access to classic scientific papers and other scholarly materials, since 1993. More About: ESP | OUR CONTENT | THIS WEBSITE | WHAT'S NEW | WHAT'S HOT
Comparative Timelines
The ESP Timeline (one of the site's most popular features) has been completely updated to allow the user to select (using the timeline controls above each column) different topics for the left and right sides of the display.
Select:
New Left Column
New Left Column
Dates
Decade
New Right Column
New Right Column
 "Bibless overalls" made of canvas are sold by the 20 year-old Levi Strauss in San Francisco. Within three years he will switch to denim and dye his pants indigo blue.
"Bibless overalls" made of canvas are sold by the 20 year-old Levi Strauss in San Francisco. Within three years he will switch to denim and dye his pants indigo blue.
1850
 German physicist Gustav Theodor Fechner discovers that an increase in the intensity of a stimulus does not produce a one-to-one increase in the intensity of sensation. Instead, the sensation seems to increase as the logarithm of the excitation.
German physicist Gustav Theodor Fechner discovers that an increase in the intensity of a stimulus does not produce a one-to-one increase in the intensity of sensation. Instead, the sensation seems to increase as the logarithm of the excitation.
Arithmometer: first commercially successful mechanical calculator launched
 The fast-acting Collodion process invented by Frederick Scott Archer. Images require only two or three seconds of light exposure. Collodion process, mostly synonymous with the "collodion wet plate process", requires the photographic material to be coated, sensitized, exposed and developed within the span of about fifteen minutes, necessitating a portable darkroom for use in the field. Collodion is normally used in its wet form, but can also be used in humid ("preserved") or dry form, at the cost of greatly increased exposure time. The latter made the dry form unsuitable for the usual portraiture work of most professional photographers of the 19th century. The use of the dry form was therefore mostly confined to landscape photography and other special applications where minutes-long exposure times were tolerable.
The fast-acting Collodion process invented by Frederick Scott Archer. Images require only two or three seconds of light exposure. Collodion process, mostly synonymous with the "collodion wet plate process", requires the photographic material to be coated, sensitized, exposed and developed within the span of about fifteen minutes, necessitating a portable darkroom for use in the field. Collodion is normally used in its wet form, but can also be used in humid ("preserved") or dry form, at the cost of greatly increased exposure time. The latter made the dry form unsuitable for the usual portraiture work of most professional photographers of the 19th century. The use of the dry form was therefore mostly confined to landscape photography and other special applications where minutes-long exposure times were tolerable.
 Isaac Singer patents the continuous-stitch sewing machine.
Isaac Singer patents the continuous-stitch sewing machine.
The Erie Railroad, now controlled by Daniel Drew, becomes the first rail line connecting the Great Lakes with New York City, and begins to compete with the Erie Canal as a transportation route.
1851
(no entry for this year)
In South Bend, Indiana, Clement and Henry Studebaker found Studebaker Brothers. Joined by a third brother, John, in 1858, the company will become the world's largest maker of wagons and carriages.
 In Sweden, safety matches are patented by J. E. Lundstrom.
In Sweden, safety matches are patented by J. E. Lundstrom.
 The brown paper bag is invented.
The brown paper bag is invented.
The elevator is invented, facilitating the future development of skyscrapers.
The U.S. state of Pennsylvania adopts a non-standard railroad gauge in order to prevent New York's Erie Railroad from establishing a route, through Pennsylvania, to Ohio.
1852
 Albrecht von Kölliker publishes the first textbook of histology, Handbuch der Gewebelehre.
Albrecht von Kölliker publishes the first textbook of histology, Handbuch der Gewebelehre.
 Hermann Ludwig von Helmholtz becomes the first to discover how fast a message travels along a nerve, measuring the speed of transmission in a frog nerve cell.
Hermann Ludwig von Helmholtz becomes the first to discover how fast a message travels along a nerve, measuring the speed of transmission in a frog nerve cell.
1853
 Rudolph Albert von Kölliker discovers the cellular origin of spermatozoa, which were believed by some to originate from a fermentation process.
Rudolph Albert von Kölliker discovers the cellular origin of spermatozoa, which were believed by some to originate from a fermentation process.
 Andr -Adolphe-Eug ne Disd ri credited with introduction of the carte de visite (English: visiting card or calling card) format for portraiture. Disd ri uses a camera with multiple lenses that can photograph eight different poses on one large negative. After printing on albumen paper, the images are cut apart and glued to calling-card-size mounts. Photographs had previously served as calling cards, but Disd ri's invention of the paper carte de visite (i.e. "visiting card") enabled the mass production of photographs. On 27 November 1854 he patented the system of printing ten photographs on a single sheet (although there is no evidence that a system printing more than eight actually materialized). Disd ri's's cartes de visite were 6 9 cm, about the size of conventional (nonphotographic) visiting cards of the time, and were made by a camera with four lenses and a sliding plate holder; a design inspired by the stereoscopic cameras. The novelty quickly spread throughout the world. According to a German visitor, Disd ri's studio became "really the Temple of Photography - a place unique in its luxury and elegance. Daily he sells three to four thousand francs worth of portraits". The fact that these photos could be reproduced inexpensively and in great quantity brought about the decline of the daguerreotype and ushered in a carte de visite craze as they became enormously popular throughout Europe and the United States. Disd ri also invented the twin-lens reflex camera.
Andr -Adolphe-Eug ne Disd ri credited with introduction of the carte de visite (English: visiting card or calling card) format for portraiture. Disd ri uses a camera with multiple lenses that can photograph eight different poses on one large negative. After printing on albumen paper, the images are cut apart and glued to calling-card-size mounts. Photographs had previously served as calling cards, but Disd ri's invention of the paper carte de visite (i.e. "visiting card") enabled the mass production of photographs. On 27 November 1854 he patented the system of printing ten photographs on a single sheet (although there is no evidence that a system printing more than eight actually materialized). Disd ri's's cartes de visite were 6 9 cm, about the size of conventional (nonphotographic) visiting cards of the time, and were made by a camera with four lenses and a sliding plate holder; a design inspired by the stereoscopic cameras. The novelty quickly spread throughout the world. According to a German visitor, Disd ri's studio became "really the Temple of Photography - a place unique in its luxury and elegance. Daily he sells three to four thousand francs worth of portraits". The fact that these photos could be reproduced inexpensively and in great quantity brought about the decline of the daguerreotype and ushered in a carte de visite craze as they became enormously popular throughout Europe and the United States. Disd ri also invented the twin-lens reflex camera.
1854
(no entry for this year)

 A mercury pump is developed by inventor Heinrich Geissler, to produce vacuum tubes. The first cathode rays will be observed in these tubes, after they are modified and improved by Sir William Crookes.
A mercury pump is developed by inventor Heinrich Geissler, to produce vacuum tubes. The first cathode rays will be observed in these tubes, after they are modified and improved by Sir William Crookes.
 Engineer Frederick Taylor carries out "time-motion" studies of workers with the idea of making their labor more efficient. He will pioneer the "scientific management" of the workplace.
Engineer Frederick Taylor carries out "time-motion" studies of workers with the idea of making their labor more efficient. He will pioneer the "scientific management" of the workplace.
1855
 Alfred Russel Wallace publishes "On the Law which has Regulated the Introduction of New Species," anticipating Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection.
Alfred Russel Wallace publishes "On the Law which has Regulated the Introduction of New Species," anticipating Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection.
 Rudolf Virchow states the principle that new cells come into being only by division of previously existing cells: Omnis cellula e cellula.
Rudolf Virchow states the principle that new cells come into being only by division of previously existing cells: Omnis cellula e cellula.
 Recherches sur la putréfaction, by Louis Pasteur, is published. The book describes how fermentation is caused by microorganisms.
Recherches sur la putréfaction, by Louis Pasteur, is published. The book describes how fermentation is caused by microorganisms.
 A railway bridge spanning the Mississippi opens between Rockville, Illinois, and Davenport, Iowa. Abraham Lincoln, a lawyer, will defend the legality of the bridge before the Supreme Court, in response to a "right of way" suit brought by a steamship company.
A railway bridge spanning the Mississippi opens between Rockville, Illinois, and Davenport, Iowa. Abraham Lincoln, a lawyer, will defend the legality of the bridge before the Supreme Court, in response to a "right of way" suit brought by a steamship company.
 During Easter vacation from London's Royal College of Chemistry, 18-year-old William Henry Perkin synthesized mauve, or aniline purple — the first synthetic dyestuff — from chemicals derived from coal tar. Mauve was enthusiastically adopted by the fashion industry in England and synthetic dyes quickly destroyed the market for natural substances derived from plants like indigo and madder. Perkin's creation was an accident — he was trying to synthesize quinine.
During Easter vacation from London's Royal College of Chemistry, 18-year-old William Henry Perkin synthesized mauve, or aniline purple — the first synthetic dyestuff — from chemicals derived from coal tar. Mauve was enthusiastically adopted by the fashion industry in England and synthetic dyes quickly destroyed the market for natural substances derived from plants like indigo and madder. Perkin's creation was an accident — he was trying to synthesize quinine.
 The "Bessemer process" for making inexpensive steel, which involves using blasts of cold air to decarbonize melted pig iron, is developed by inventor Henry Bessemer.
The "Bessemer process" for making inexpensive steel, which involves using blasts of cold air to decarbonize melted pig iron, is developed by inventor Henry Bessemer.
The 458-mile Wabash and Erie Canal opens after 24 years, and is the largest canal ever dug in the U.S. By 1860, however, sections will begin to be close, and, unable to compete for railroads, the entire Canal will be closed by 1874.
1856
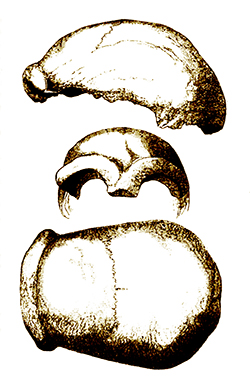 The remains of the first known example of what come to be known as the "Neanderthals" is found in a cave near Düsseldorf, in the Neander Valley. The discovery was made by limestone quarry miners and consists of a skullcap, two femora, the three right arm bones, two of the left arm bones, ilium, and fragments of a scapula and ribs. The fossils were given to Johann Carl Fuhlrott, a local teacher and amateur naturalist. The first description of the remains was made by anatomist Hermann Schaaffhausen and the find was announced jointly in 1857.In 1997, the specimen was the first to yield Neanderthal mitochondrial DNA fragments. The description of this discovery represents the beginning of paleoanthropology as a scientific discipline.
The remains of the first known example of what come to be known as the "Neanderthals" is found in a cave near Düsseldorf, in the Neander Valley. The discovery was made by limestone quarry miners and consists of a skullcap, two femora, the three right arm bones, two of the left arm bones, ilium, and fragments of a scapula and ribs. The fossils were given to Johann Carl Fuhlrott, a local teacher and amateur naturalist. The first description of the remains was made by anatomist Hermann Schaaffhausen and the find was announced jointly in 1857.In 1997, the specimen was the first to yield Neanderthal mitochondrial DNA fragments. The description of this discovery represents the beginning of paleoanthropology as a scientific discipline.
Louis Agassiz publishes Essay on Classification advocating a theory of multiple creations and contradicting both evolution and Noah's ark.
 Gregor Mendel, a monk at the Augustinian monastery of St. Thomas in Brünn, Austria (now Brno, Czechoslovakia), begins breeding experiments with the garden pea, Pisum sativum.
Gregor Mendel, a monk at the Augustinian monastery of St. Thomas in Brünn, Austria (now Brno, Czechoslovakia), begins breeding experiments with the garden pea, Pisum sativum.
Heinz Christian Pander describes conodonts — toothy microfossils that will puzzle paleontologists for many years.
 In Burrville, Connecticut, commercial production of Gail Borden's patented "condensed milk" begins. The product is made from skim milk, without any fat and without a number of nutrients found in cow's milk.
In Burrville, Connecticut, commercial production of Gail Borden's patented "condensed milk" begins. The product is made from skim milk, without any fat and without a number of nutrients found in cow's milk.
In California, Tokay, Zinfandel, and Shiraz grapes (all from Hungary) are first planted, and Italian honeybees are introduced. This is the beginning of the U.S. wine and honey industries. In North America, honey bees are an artificially introduced and invasive species.
 Robert Wilhelm von Bunsen (along with Henry Roscoe) publish a design for a laboratory burner in Poggendorff's Annalen der Physik und Chemie, 100:84-85.
Robert Wilhelm von Bunsen (along with Henry Roscoe) publish a design for a laboratory burner in Poggendorff's Annalen der Physik und Chemie, 100:84-85.
1857
(no entry for this year)
J. Schweppe & Co. Ltd. patents a quinine tonic water that they will begin selling in 1880.
 John Landis Mason patents a reusable glass jar.
John Landis Mason patents a reusable glass jar.
1858
Rudolf Virchow finalizes the cell theory originally announced by Schleiden and Schwann 11 years earlier by declaring that cells are the basic units of all living things, and all cells are formed by the division of existing cells.
 Alfred Russel Wallace sends to Darwin a manuscript — "On the Tendency of Varieties to Depart Indefinitely from the Original Type" — that shows clearly that Wallace has independently formulated a model of evolution by natural selection.
Alfred Russel Wallace sends to Darwin a manuscript — "On the Tendency of Varieties to Depart Indefinitely from the Original Type" — that shows clearly that Wallace has independently formulated a model of evolution by natural selection.

 Darwin's and Wallace's ideas are jointly presented to the Linnaean Society of London.
Darwin's and Wallace's ideas are jointly presented to the Linnaean Society of London.
The first relatively complete dinosaur skeleton, of Hadrosaurus foulkii, is found in New Jersey.
 Physician Henry Gray publishes Anatomy of the Human Body, Descriptive and Surgical. Gray's Anatomy will be a standard textbook of anatomy for more than a century.
Physician Henry Gray publishes Anatomy of the Human Body, Descriptive and Surgical. Gray's Anatomy will be a standard textbook of anatomy for more than a century.
 In Titusville, Pennsylvania, commercial production of petroleum begins, with drilling of the first well by Edwin Laurentine Drake. The well will produce approximately 400 gallons/day.
In Titusville, Pennsylvania, commercial production of petroleum begins, with drilling of the first well by Edwin Laurentine Drake. The well will produce approximately 400 gallons/day.
 The first internal combustion engine is developed by Jean-Joseph-Etienne Lenoir. The engine uses coal gas.
The first internal combustion engine is developed by Jean-Joseph-Etienne Lenoir. The engine uses coal gas.
1859
 Charles Darwin publishes On the Origin of Species.
Charles Darwin publishes On the Origin of Species.
An exceptionally well-preserved skeleton is discovered in Bavaria. Two years later, this bird-like, bipedal dinosaur will be named Compsognathus, meaning "dainty jaw."
Catholic priest Jean-Jacques Pouech describes fossil eggshell fragments. They will eventually prove to be the first described dinosaur eggs.
ESP Quick Facts
ESP Origins
In the early 1990's, Robert Robbins was a faculty member at Johns Hopkins, where he directed the informatics core of GDB — the human gene-mapping database of the international human genome project. To share papers with colleagues around the world, he set up a small paper-sharing section on his personal web page. This small project evolved into The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Support
In 1995, Robbins became the VP/IT of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, WA. Soon after arriving in Seattle, Robbins secured funding, through the ELSI component of the US Human Genome Project, to create the original ESP.ORG web site, with the formal goal of providing free, world-wide access to the literature of classical genetics.
ESP Rationale
Although the methods of molecular biology can seem almost magical to the uninitiated, the original techniques of classical genetics are readily appreciated by one and all: cross individuals that differ in some inherited trait, collect all of the progeny, score their attributes, and propose mechanisms to explain the patterns of inheritance observed.
ESP Goal
In reading the early works of classical genetics, one is drawn, almost inexorably, into ever more complex models, until molecular explanations begin to seem both necessary and natural. At that point, the tools for understanding genome research are at hand. Assisting readers reach this point was the original goal of The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Usage
Usage of the site grew rapidly and has remained high. Faculty began to use the site for their assigned readings. Other on-line publishers, ranging from The New York Times to Nature referenced ESP materials in their own publications. Nobel laureates (e.g., Joshua Lederberg) regularly used the site and even wrote to suggest changes and improvements.
ESP Content
When the site began, no journals were making their early content available in digital format. As a result, ESP was obliged to digitize classic literature before it could be made available. For many important papers — such as Mendel's original paper or the first genetic map — ESP had to produce entirely new typeset versions of the works, if they were to be available in a high-quality format.
ESP Help
Early support from the DOE component of the Human Genome Project was critically important for getting the ESP project on a firm foundation. Since that funding ended (nearly 20 years ago), the project has been operated as a purely volunteer effort. Anyone wishing to assist in these efforts should send an email to Robbins.
ESP Plans
With the development of methods for adding typeset side notes to PDF files, the ESP project now plans to add annotated versions of some classical papers to its holdings. We also plan to add new reference and pedagogical material. We have already started providing regularly updated, comprehensive bibliographies to the ESP.ORG site.
ESP Picks from Around the Web (updated 06 MAR 2017 )
Old Science

Weird Science

Treating Disease with Fecal Transplantation
Fossils of miniature humans (hobbits) discovered in Indonesia

Dinosaur tail, complete with feathers, found preserved in amber.
Astronomy

Mysterious fast radio burst (FRB) detected in the distant universe.