MENU
The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project: Providing access to classic scientific papers and other scholarly materials, since 1993. More About: ESP | OUR CONTENT | THIS WEBSITE | WHAT'S NEW | WHAT'S HOT
Comparative Timelines
The ESP Timeline (one of the site's most popular features) has been completely updated to allow the user to select (using the timeline controls above each column) different topics for the left and right sides of the display.
Select:
New Left Column
New Left Column
Dates
Decade
New Right Column
New Right Column
 Louis Agassiz attacks Darwin's the origin of species, rejecting the idea of evolution of the species and arguing that each species was created separately.
Louis Agassiz attacks Darwin's the origin of species, rejecting the idea of evolution of the species and arguing that each species was created separately.
 Thomas Henry Huxley (sometimes known as Darwin's bulldog) clashes with Bishop "Soapy Sam" Wilberforce about evolution at the annual meeting of The British Association for the Advancement of Science, in what has come to be known as the Huxley-Wilberforce debate.
Thomas Henry Huxley (sometimes known as Darwin's bulldog) clashes with Bishop "Soapy Sam" Wilberforce about evolution at the annual meeting of The British Association for the Advancement of Science, in what has come to be known as the Huxley-Wilberforce debate.
Bishop Wilberforce is supposed to have asked Huxley sarcastically whether "it was through his grandfather or his grandmother that he claimed descent from a monkey." Huxley responded, "If then the question is put to me whether I would rather have a miserable ape for a grandfather or a man highly endowed by nature and possessed of great means of influence and yet employs these faculties and that influence for the mere purpose of introducing ridicule into a grave scientific discussion, I unhesitatingly affirm my preference for the ape." Or words to that effect.
John Phillips diagrams the progressive but fluctuating diversity of life on Earth based on the fossil record. His work evidences massive extinctions at the end of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic, and increased diversity in each subsequent age.
 Louis Pasteur becomes significantly involved in biological research with the publication of "Mémoir sur la fermentation alcoolique" in which he showed that alcoholic fermentation seemed to be carried out by yeast, which were themselves living organisms.
Louis Pasteur becomes significantly involved in biological research with the publication of "Mémoir sur la fermentation alcoolique" in which he showed that alcoholic fermentation seemed to be carried out by yeast, which were themselves living organisms.
Herman Hollerith was born 29th February 1860
 Emil Erlenmeyer invents the flask.
Emil Erlenmeyer invents the flask.
1860
Herman Hollerith was born 29th February 1860
 Emil Erlenmeyer invents the flask.
Emil Erlenmeyer invents the flask.

 Between 1861 and 1862, Max Johann Sigismund Schultze (Germany) and Heinrich Anton de Bary (Germany) establish the essential unity of protoplasm in all living cells.
Between 1861 and 1862, Max Johann Sigismund Schultze (Germany) and Heinrich Anton de Bary (Germany) establish the essential unity of protoplasm in all living cells.
 First recognized fossil Archaeopteryx lithographica skeleton is found in the stone quarries of Solnhofen.
First recognized fossil Archaeopteryx lithographica skeleton is found in the stone quarries of Solnhofen.
 In "Mémoires sur les corpuscles organisés qui existent dans l'atmosphère," Pasteur applies heat to bent-neck flasks to show unequivocally that the "organized bodies" (microbes) which drive fermentation originate from "organized bodies" that exist in the atmosphere. In this elegant series of experiments, Pasteur laid to rest the long-held belief in spontaneous generation."
In "Mémoires sur les corpuscles organisés qui existent dans l'atmosphère," Pasteur applies heat to bent-neck flasks to show unequivocally that the "organized bodies" (microbes) which drive fermentation originate from "organized bodies" that exist in the atmosphere. In this elegant series of experiments, Pasteur laid to rest the long-held belief in spontaneous generation."
In his presidential address to the Geological Society of London, Leonard Horner proposes removing the world's "creation" date of 4004 BC from the English Bible, citing geological evidence of a much older planet.
 Oliver Wendell Holmes invents stereoscope viewer
Oliver Wendell Holmes invents stereoscope viewer
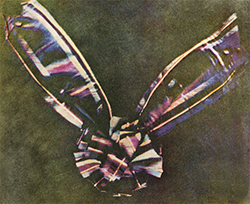 James Clerk Maxwell presents a projected additive color image of a multicolored ribbon, the first demonstration of color photography by the three-color method he suggested in 1855. It uses three separate black-and-white photographs taken and projected through red, green and blue color filters. The projected image is temporary but the set of three "color separations" is the first durable color photograph.
James Clerk Maxwell presents a projected additive color image of a multicolored ribbon, the first demonstration of color photography by the three-color method he suggested in 1855. It uses three separate black-and-white photographs taken and projected through red, green and blue color filters. The projected image is temporary but the set of three "color separations" is the first durable color photograph.
1861
 Oliver Wendell Holmes invents stereoscope viewer
Oliver Wendell Holmes invents stereoscope viewer
 James Clerk Maxwell presents a projected additive color image of a multicolored ribbon, the first demonstration of color photography by the three-color method he suggested in 1855. It uses three separate black-and-white photographs taken and projected through red, green and blue color filters. The projected image is temporary but the set of three "color separations" is the first durable color photograph.
James Clerk Maxwell presents a projected additive color image of a multicolored ribbon, the first demonstration of color photography by the three-color method he suggested in 1855. It uses three separate black-and-white photographs taken and projected through red, green and blue color filters. The projected image is temporary but the set of three "color separations" is the first durable color photograph.
Lord Kelvin asserts that the Earth and sun are cooling from their initial formation, between 20 and 400 million years ago. He will later adopt the smaller number.
1862
(no entry for this year)
Anti-evolutionist James Hunt, founder of the Anthropological Society of London, gives a presidential address to the society stating that human races were created separately. He further argues that the African species is closer in ability to apes than to Europeans.
Alfred Russel Wallace describes the "Wallace line," the dividing line between Indo-Malayan and Austro-Malayan fauna, in Proceedings of the Royal Geographical Society of London.

 Dominique Alexandre Godron and Charles Victor Naudin (France) independently report experiments in plant hybridization. Naudin confirmed Sageret's work, in general discussed work of the early hybridizers, and reported dominance and segregation in Datura (jimsonweed) hybrids. He did not deal with single characters and reported no statistical observations on the second generation. His theoretical explanation of his facts was a forerunner of Mendel's ideas, but inferred rather than deduced.
Dominique Alexandre Godron and Charles Victor Naudin (France) independently report experiments in plant hybridization. Naudin confirmed Sageret's work, in general discussed work of the early hybridizers, and reported dominance and segregation in Datura (jimsonweed) hybrids. He did not deal with single characters and reported no statistical observations on the second generation. His theoretical explanation of his facts was a forerunner of Mendel's ideas, but inferred rather than deduced.
T. H. Huxley publishes Man's Place in Nature discussing human and primate paleontology, and showing similarities between humans and other animals.
 Father-and-son glassworkers Leopold and Rudolf Blaschka begin making glass models of marine invertebrates. Marine biologists will refer to their exquisitely detailed, accurate models 150 years later while trying to see how many of the depicted species can still be found in the wild.
Father-and-son glassworkers Leopold and Rudolf Blaschka begin making glass models of marine invertebrates. Marine biologists will refer to their exquisitely detailed, accurate models 150 years later while trying to see how many of the depicted species can still be found in the wild.
Abraham Lincoln forms the National Academy of Sciences.
1863
(no entry for this year)
 Ernst Haeckel (Häckel) outlines the essential elements of modern zoological classification.
Ernst Haeckel (Häckel) outlines the essential elements of modern zoological classification.
 James Clerk Maxwell's A dynamical theory of the electromagnetic field is the first of his publications to use Michael Faraday's concept of a field as the basis of the mathematical treatment of electricity and magnetism. It introduces Maxwell's equations to describe electromagnetism.
James Clerk Maxwell's A dynamical theory of the electromagnetic field is the first of his publications to use Michael Faraday's concept of a field as the basis of the mathematical treatment of electricity and magnetism. It introduces Maxwell's equations to describe electromagnetism.
1864
(no entry for this year)
John Lubbock publishes Prehistoric Times dividing what has previously been understood to be the Stone Age into two parts: the older Paleolithic and the newer Neolithic. In the same book, he also argues that modern Tasmanians and Fuegians are throwbacks to archaic humans.
Franz Schweigger-Seidel and A. von la Valette St. George (Germany) independently prove that a spermatozoon is a single cell and contains nucleus and cytoplasm
 Gregor Mendel presents his work on inheritance in peas to the Brünn Natural History Society. The results are published the following year.
Gregor Mendel presents his work on inheritance in peas to the Brünn Natural History Society. The results are published the following year.
Sir John William Dawson of McGill University identifies "shells" of huge foraminiferal protozoans. Known as Eozoön or "dawn animal," this find is used as an argument against evolution because it shows a relatively "modern" animal early in the fossil record. It will prove, however, to be a geologically young pseudofossil formed by heat and pressure on limestone.
Paolo Mantegazza publishes Degli Innesti Animali e della Produzione Artificiale delle Cellule (On Animal Grafts and Artificial Cell Production) describing the results of a series of interspecies animal grafts, such as the transplant of a cockspur onto a cow ear. Grafts described include transplants between dogs, frogs and rodents. Mantegazza reports that some grafts decomposed while others became "pathological tumours."
 Rudolf Clausius invents the term ENTROPY to describe the degradation of energy in the closed system.
Rudolf Clausius invents the term ENTROPY to describe the degradation of energy in the closed system.
1865
(no entry for this year)
German zoologist Ernst Haeckel publishes General Morphology of Organisms, the first detailed genealogical tree relating all known organisms, incorporating the principles of Darwinian evolution.
 Ernst Heinrich Haeckel (Häckel) hypothesizes that the nucleus of a cell transmits its hereditary information.
Ernst Heinrich Haeckel (Häckel) hypothesizes that the nucleus of a cell transmits its hereditary information.
 Mendel publishes his work on heredity, Versuche über Pflanzen Hybriden.
Mendel publishes his work on heredity, Versuche über Pflanzen Hybriden.
 Ernst Heinrich Haeckel (Häckel) first used the term ECOLOGY to describe the study of living organisms and their interactions with other organisms and with their environment.
Ernst Heinrich Haeckel (Häckel) first used the term ECOLOGY to describe the study of living organisms and their interactions with other organisms and with their environment.
1866
(no entry for this year)
Orléans Railway Company employee Peccadeau de l'Isle presents a paper to the French Academy of Sciences on his recent discoveries at Montastruc, including a mammoth carved from a reindeer antler, and two reindeer (found in separate pieces) carved from a mammoth tusk. The finds will eventually be dated at about 13,000 years old.
H. S. Bidwell (United States) reports controlled pollination in maize.
1867
(no entry for this year)
 Charles Darwin publishes The Variation of Animals and Plants under Domestication, in which he offers his own theory of heredity, which he called the "Provisional Hypothesis of Pangenesis."
Charles Darwin publishes The Variation of Animals and Plants under Domestication, in which he offers his own theory of heredity, which he called the "Provisional Hypothesis of Pangenesis."
Ernst Haeckel publishes Natürliche Schöpfungsgeschichte, subdividing humanity into 12 separate species. He also asserts that evolution consists of 22 phases, the 21st being the "missing link" between apes and humans.
Thomas Henry Huxley publishes "On the Animals which are Most Nearly Intermediate between Birds and Reptiles," arguing that birds are descendants of dinosaurs. This suggestion will not be taken very seriously for another century.
Three human skulls and other skeletal remains, roughly 30,000 years old, are discovered at a rock shelter called Cro-Magnon (old French for "big hole").
 Louis Ducos du Hauron patents his numerous ideas for color photography based on the three-color principle, including procedures for making subtractive color prints on paper. They are published the following year. Their implementation is not technologically practical at that time, but they anticipate most of the color processes that are later introduced.
Louis Ducos du Hauron patents his numerous ideas for color photography based on the three-color principle, including procedures for making subtractive color prints on paper. They are published the following year. Their implementation is not technologically practical at that time, but they anticipate most of the color processes that are later introduced.
Wallace Clement Ware Sabine becomes the first acoustical engineer and uses acoustic principles to design Boston's Symphony Hall.
1868
 Louis Ducos du Hauron patents his numerous ideas for color photography based on the three-color principle, including procedures for making subtractive color prints on paper. They are published the following year. Their implementation is not technologically practical at that time, but they anticipate most of the color processes that are later introduced.
Louis Ducos du Hauron patents his numerous ideas for color photography based on the three-color principle, including procedures for making subtractive color prints on paper. They are published the following year. Their implementation is not technologically practical at that time, but they anticipate most of the color processes that are later introduced.
Wallace Clement Ware Sabine becomes the first acoustical engineer and uses acoustic principles to design Boston's Symphony Hall.
 Francis Galton publishes Hereditary Genius. In it he describes a scientific study of human pedigrees from which he concludes that intelligence has a genetic basis.
Francis Galton publishes Hereditary Genius. In it he describes a scientific study of human pedigrees from which he concludes that intelligence has a genetic basis.
Huxley, Norman Lockyer and others found Nature Magazine, which becomes one of the world's two most important scientific journals. (The other journal is Science.)
1869
(no entry for this year)
ESP Quick Facts
ESP Origins
In the early 1990's, Robert Robbins was a faculty member at Johns Hopkins, where he directed the informatics core of GDB — the human gene-mapping database of the international human genome project. To share papers with colleagues around the world, he set up a small paper-sharing section on his personal web page. This small project evolved into The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Support
In 1995, Robbins became the VP/IT of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, WA. Soon after arriving in Seattle, Robbins secured funding, through the ELSI component of the US Human Genome Project, to create the original ESP.ORG web site, with the formal goal of providing free, world-wide access to the literature of classical genetics.
ESP Rationale
Although the methods of molecular biology can seem almost magical to the uninitiated, the original techniques of classical genetics are readily appreciated by one and all: cross individuals that differ in some inherited trait, collect all of the progeny, score their attributes, and propose mechanisms to explain the patterns of inheritance observed.
ESP Goal
In reading the early works of classical genetics, one is drawn, almost inexorably, into ever more complex models, until molecular explanations begin to seem both necessary and natural. At that point, the tools for understanding genome research are at hand. Assisting readers reach this point was the original goal of The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Usage
Usage of the site grew rapidly and has remained high. Faculty began to use the site for their assigned readings. Other on-line publishers, ranging from The New York Times to Nature referenced ESP materials in their own publications. Nobel laureates (e.g., Joshua Lederberg) regularly used the site and even wrote to suggest changes and improvements.
ESP Content
When the site began, no journals were making their early content available in digital format. As a result, ESP was obliged to digitize classic literature before it could be made available. For many important papers — such as Mendel's original paper or the first genetic map — ESP had to produce entirely new typeset versions of the works, if they were to be available in a high-quality format.
ESP Help
Early support from the DOE component of the Human Genome Project was critically important for getting the ESP project on a firm foundation. Since that funding ended (nearly 20 years ago), the project has been operated as a purely volunteer effort. Anyone wishing to assist in these efforts should send an email to Robbins.
ESP Plans
With the development of methods for adding typeset side notes to PDF files, the ESP project now plans to add annotated versions of some classical papers to its holdings. We also plan to add new reference and pedagogical material. We have already started providing regularly updated, comprehensive bibliographies to the ESP.ORG site.
ESP Picks from Around the Web (updated 06 MAR 2017 )
Old Science

Weird Science

Treating Disease with Fecal Transplantation
Fossils of miniature humans (hobbits) discovered in Indonesia

Dinosaur tail, complete with feathers, found preserved in amber.
Astronomy

Mysterious fast radio burst (FRB) detected in the distant universe.