MENU
The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project: Providing access to classic scientific papers and other scholarly materials, since 1993. More About: ESP | OUR CONTENT | THIS WEBSITE | WHAT'S NEW | WHAT'S HOT
Comparative Timelines
The ESP Timeline (one of the site's most popular features) has been completely updated to allow the user to select (using the timeline controls above each column) different topics for the left and right sides of the display.
Select:
New Left Column
New Left Column
Dates
Decade
New Right Column
New Right Column
South Carolina passes the first comprehensive slave codes.
Virginia passes the first anti-miscegenation law, forbidding marriages between whites and blacks or whites and Native Americans.
Virginia prohibits the manumission of slaves within its borders. Manumitted slaves are forced to leave the colony.
1691
(no entry for this year)
The colonies of Plymouth and Massachusetts are united.
Witchcraft mania begins to take over new England.
1692
(no entry for this year)
The College of William and Mary is founded in Williamsburg, Virginia, by a royal charter.
1693
Naturalist John Ray publishes Three Physicotheological Discourses about the Creation, the Deluge and the Conflagration, discussing conflicting theories about the nature of fossils.
Rice cultivation is introduced into Carolina. Slave importation increases dramatically.
The Bank of England is established.
1694
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1695
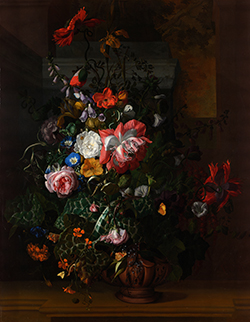 Painting by Rachel Ruysch: Flowers on a Ledge. Ruysch's skill lay in the minute observation of each flower in a totally realistic way which is then composed into an elaborate arrangement which would be very difficult to achieve in nature, as the flowers would not support each other so well under such an arrangement. In common with most flower pieces from the last third of the 17th century, the colors of the flowers are much more carefully balanced than in the earlier pictures.
Painting by Rachel Ruysch: Flowers on a Ledge. Ruysch's skill lay in the minute observation of each flower in a totally realistic way which is then composed into an elaborate arrangement which would be very difficult to achieve in nature, as the flowers would not support each other so well under such an arrangement. In common with most flower pieces from the last third of the 17th century, the colors of the flowers are much more carefully balanced than in the earlier pictures.
The Royal African Trade Company loses its monopoly and New England colonists enter the slave trade.
1696
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1697
Scandinavian historian Olof Rudbeck publishes his attempt to chronologically measure sedimentary deposits, laying the foundations for the field of stratigraphy.
Calcutta is founded by the English.
1698
Edward Lhwyd publishes a description of a "flatfish" in the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society. (The flatfish is really a trilobite, an ancient marine arthropod.)
(no entry for this year)
1699
 Painting by Alexandre-François Desportes: Autoportrait en chasseur (Self-portrait as hunter). Desportes was born in Champigneulle, Ardennes. He studied in Paris, in the studio of the Flemish painter Nicasius Bernaerts, a pupil of Frans Snyders. During a brief sojourn in Poland, 1695–1696, he painted portraits of John III Sobieski and Polish aristocrats; after the king's death Desportes returned to Paris, convinced that he should specialise in animals and flowers. He was received by the Académie de peinture et de sculpture in 1699, with the Self-Portrait in Hunting Dress now in the Musée du Louvre. In 1712–1713 he spent six months in England. He received many commissions for decorative panels for the royal chateaux: Versailles, Marly, Meudon, Compiègne and, his last royal commission, for Louis XV at Choisy, 1742. He also did decorative paintings for the duc de Bourbon at Chantilly. Both Louis XIV and Louis XV commissioned portraits of their favorite hunting dogs.
Painting by Alexandre-François Desportes: Autoportrait en chasseur (Self-portrait as hunter). Desportes was born in Champigneulle, Ardennes. He studied in Paris, in the studio of the Flemish painter Nicasius Bernaerts, a pupil of Frans Snyders. During a brief sojourn in Poland, 1695–1696, he painted portraits of John III Sobieski and Polish aristocrats; after the king's death Desportes returned to Paris, convinced that he should specialise in animals and flowers. He was received by the Académie de peinture et de sculpture in 1699, with the Self-Portrait in Hunting Dress now in the Musée du Louvre. In 1712–1713 he spent six months in England. He received many commissions for decorative panels for the royal chateaux: Versailles, Marly, Meudon, Compiègne and, his last royal commission, for Louis XV at Choisy, 1742. He also did decorative paintings for the duc de Bourbon at Chantilly. Both Louis XIV and Louis XV commissioned portraits of their favorite hunting dogs.
Edward Lhwyd publishes a book devoted to British fossils. In it, he describes ichthyosaur remains as those of a fish.
Based on a dissection he performed the year before, Edward Tyson publishes Orang Outan, sive Homo sylvestris pointing out similarities between chimpanzee and human anatomy. (Although he has dissected an infant chimp, Tyson uses the term "orang-outan.")
ESP Quick Facts
ESP Origins
In the early 1990's, Robert Robbins was a faculty member at Johns Hopkins, where he directed the informatics core of GDB — the human gene-mapping database of the international human genome project. To share papers with colleagues around the world, he set up a small paper-sharing section on his personal web page. This small project evolved into The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Support
In 1995, Robbins became the VP/IT of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, WA. Soon after arriving in Seattle, Robbins secured funding, through the ELSI component of the US Human Genome Project, to create the original ESP.ORG web site, with the formal goal of providing free, world-wide access to the literature of classical genetics.
ESP Rationale
Although the methods of molecular biology can seem almost magical to the uninitiated, the original techniques of classical genetics are readily appreciated by one and all: cross individuals that differ in some inherited trait, collect all of the progeny, score their attributes, and propose mechanisms to explain the patterns of inheritance observed.
ESP Goal
In reading the early works of classical genetics, one is drawn, almost inexorably, into ever more complex models, until molecular explanations begin to seem both necessary and natural. At that point, the tools for understanding genome research are at hand. Assisting readers reach this point was the original goal of The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Usage
Usage of the site grew rapidly and has remained high. Faculty began to use the site for their assigned readings. Other on-line publishers, ranging from The New York Times to Nature referenced ESP materials in their own publications. Nobel laureates (e.g., Joshua Lederberg) regularly used the site and even wrote to suggest changes and improvements.
ESP Content
When the site began, no journals were making their early content available in digital format. As a result, ESP was obliged to digitize classic literature before it could be made available. For many important papers — such as Mendel's original paper or the first genetic map — ESP had to produce entirely new typeset versions of the works, if they were to be available in a high-quality format.
ESP Help
Early support from the DOE component of the Human Genome Project was critically important for getting the ESP project on a firm foundation. Since that funding ended (nearly 20 years ago), the project has been operated as a purely volunteer effort. Anyone wishing to assist in these efforts should send an email to Robbins.
ESP Plans
With the development of methods for adding typeset side notes to PDF files, the ESP project now plans to add annotated versions of some classical papers to its holdings. We also plan to add new reference and pedagogical material. We have already started providing regularly updated, comprehensive bibliographies to the ESP.ORG site.
ESP Picks from Around the Web (updated 06 MAR 2017 )
Old Science

Weird Science

Treating Disease with Fecal Transplantation
Fossils of miniature humans (hobbits) discovered in Indonesia

Dinosaur tail, complete with feathers, found preserved in amber.
Astronomy

Mysterious fast radio burst (FRB) detected in the distant universe.