MENU
The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project: Providing access to classic scientific papers and other scholarly materials, since 1993. More About: ESP | OUR CONTENT | THIS WEBSITE | WHAT'S NEW | WHAT'S HOT
Comparative Timelines
The ESP Timeline (one of the site's most popular features) has been completely updated to allow the user to select (using the timeline controls above each column) different topics for the left and right sides of the display.
Select:
New Left Column
New Left Column
Dates
Decade
New Right Column
New Right Column
(no entry for this year)
1901
 Eug ne Atget: Marchand d'Abat-Jours, an albumen silver print, now in the J. Paul Getty Museum.
Eug ne Atget: Marchand d'Abat-Jours, an albumen silver print, now in the J. Paul Getty Museum.
 Painting by Gustav Klimt: Judith and the Head of Holofernes (also known as Judith I) depicts the biblical character of Judith holding the severed head of Holofernes. Judith I reveals a curious symbolic and compositional consonance with The Sin by Franz Stuck: the temptation illustrated by the German painter becomes the model for Klimt's femme fatale by suggesting the posture of the disrobed and evanescent body as focal piece of the canvas, as well as the facial set. Judith's force originates from the close-up and the solidity of posture, rendered by the orthogonal projection of lines: to the body's verticality (and that of Holofernes') corresponds to the horizontal parallels in the lower margin: those of the arm, the shoulders joined by the collier, and finally the hair base.
Painting by Gustav Klimt: Judith and the Head of Holofernes (also known as Judith I) depicts the biblical character of Judith holding the severed head of Holofernes. Judith I reveals a curious symbolic and compositional consonance with The Sin by Franz Stuck: the temptation illustrated by the German painter becomes the model for Klimt's femme fatale by suggesting the posture of the disrobed and evanescent body as focal piece of the canvas, as well as the facial set. Judith's force originates from the close-up and the solidity of posture, rendered by the orthogonal projection of lines: to the body's verticality (and that of Holofernes') corresponds to the horizontal parallels in the lower margin: those of the arm, the shoulders joined by the collier, and finally the hair base.
(no entry for this year)
1902
(no entry for this year)
1903
 Richard Steiff designs the first teddy bears, named after Pres. Teddy Roosevelt.
Richard Steiff designs the first teddy bears, named after Pres. Teddy Roosevelt.
 Painting by Pablo Picasso: The Old Guitarist depicts an old, blind, haggard man with threadbare clothing weakly hunched over his guitar, playing in the streets of Barcelona, Spain. It is currently on display in the Art Institute of Chicago as part of the Helen Birch Bartlett Memorial Collection. At the time of The Old Guitarist's creation, Modernism, Impressionism, Post-Impressionism, and Symbolism had merged and created an overall movement called Expressionism which greatly influenced Picasso's style. Furthermore, El Greco, Picasso's poor standard of living, and the suicide of a dear friend influenced Picasso's style at the time which came to be known as his Blue Period. In the early 1960s, nearly forty percent of all college dorm rooms had a poster of this painting on the wall.
Painting by Pablo Picasso: The Old Guitarist depicts an old, blind, haggard man with threadbare clothing weakly hunched over his guitar, playing in the streets of Barcelona, Spain. It is currently on display in the Art Institute of Chicago as part of the Helen Birch Bartlett Memorial Collection. At the time of The Old Guitarist's creation, Modernism, Impressionism, Post-Impressionism, and Symbolism had merged and created an overall movement called Expressionism which greatly influenced Picasso's style. Furthermore, El Greco, Picasso's poor standard of living, and the suicide of a dear friend influenced Picasso's style at the time which came to be known as his Blue Period. In the early 1960s, nearly forty percent of all college dorm rooms had a poster of this painting on the wall.
(no entry for this year)
1904
 Photograph by Edward Steichen: The Flatiron Building depicts the recently erected Flatiron Building in New York, taking inspiration from fellow photographers like Alfred Stieglitz, who had just photographed the building a year prior. The original negative was made in 1904 and spawned three platinum-gum exhibition prints in brown (1905), blue-green (1909), and yellow-green-black (1904–1909; uncertain).  Using different proportions of pigments in each gum process, Steichen was able to create these three unique platinum-gum prints. The photograph's most notable variant is the blue-green version, which, according to Penelope Niven, became "widely reproduced from 1909 onward" because of its intense color contrasts. The significance of the prints as a whole comes from how they showcase what Niven refers to as the "artistic potential" of photography. The work is one of the best-known photographs of Steichen's Pictorialist phase.
Photograph by Edward Steichen: The Flatiron Building depicts the recently erected Flatiron Building in New York, taking inspiration from fellow photographers like Alfred Stieglitz, who had just photographed the building a year prior. The original negative was made in 1904 and spawned three platinum-gum exhibition prints in brown (1905), blue-green (1909), and yellow-green-black (1904–1909; uncertain).  Using different proportions of pigments in each gum process, Steichen was able to create these three unique platinum-gum prints. The photograph's most notable variant is the blue-green version, which, according to Penelope Niven, became "widely reproduced from 1909 onward" because of its intense color contrasts. The significance of the prints as a whole comes from how they showcase what Niven refers to as the "artistic potential" of photography. The work is one of the best-known photographs of Steichen's Pictorialist phase.
 Painting by Henri Matisse: Luxe, Calme et Volupt is an oil painting by the French artist Henri Matisse. Both foundational in the oeuvre of Matisse and a pivotal work in the history of art, Luxe, Calme et Volupt is considered the starting point of Fauvism. Luxe, Calme et Volupt was painted by artist called Matisse in 1904, after a summer spent working in St. Tropez on the French Riviera alongside the neo-Impressionist painters Paul Signac and Henri-Edmond Cross. The painting is Matisse's most important work in which he used the Divisionist technique advocated by Signac.
Painting by Henri Matisse: Luxe, Calme et Volupt is an oil painting by the French artist Henri Matisse. Both foundational in the oeuvre of Matisse and a pivotal work in the history of art, Luxe, Calme et Volupt is considered the starting point of Fauvism. Luxe, Calme et Volupt was painted by artist called Matisse in 1904, after a summer spent working in St. Tropez on the French Riviera alongside the neo-Impressionist painters Paul Signac and Henri-Edmond Cross. The painting is Matisse's most important work in which he used the Divisionist technique advocated by Signac.
 Painting by Maxfield Parrish: The Dinky Bird, an illustration from Poems of Childhood exemplifies Parrish's characteristic use of androgynous figures. To a modern eye, Parrish's early work — characterized by himself as "girls on rocks" — may bring to mind the words kitsch or schlock or schmaltz or maudlin, but to many who were enduring the Great Depression or World War II, his images, like Busby Berkeley musicals, inspired a bit of hope — an imagining that things did not always have to be this bad. During those hard times, many a lower middle class American living room had one or more cheap Parrish prints, sometimes just a page from a magazine, adorning the wall.
Painting by Maxfield Parrish: The Dinky Bird, an illustration from Poems of Childhood exemplifies Parrish's characteristic use of androgynous figures. To a modern eye, Parrish's early work — characterized by himself as "girls on rocks" — may bring to mind the words kitsch or schlock or schmaltz or maudlin, but to many who were enduring the Great Depression or World War II, his images, like Busby Berkeley musicals, inspired a bit of hope — an imagining that things did not always have to be this bad. During those hard times, many a lower middle class American living room had one or more cheap Parrish prints, sometimes just a page from a magazine, adorning the wall.
K. S. Merezhkovsky suggests that chloroplasts originated as a cyanobacterium swallowed by a protozoan, i.e., algal and plant cells result from two independent organisms that became symbionts. The idea will be largely forgotten until it is suggested again in the 1960s.
1905
 Painting by Gustav Klimt: Margaret "Gretl" Stonborough-Wittgenstein. Stonborough-Wittgenstein, a member of the prominent and wealthy Viennese Wittgenstein family, was a sister of the philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein and the pianist Paul Wittgenstein. She was the subject of a portrait painted for her wedding by the artist Gustav Klimt (Stonborough-Wittgenstein and other members of the Wittgenstein family were among Klimt's most important patrons), which was sold in 1960 by her son Thomas and may now be seen in the Neue Pinakothek gallery in Munich. Aside: The painting appears briefly behind Ava, an AI robot, in the film Ex Machina (a film that is an excellent exploration of artificial intelligence, the nature of consciousness, and passing a Turing Test).
Painting by Gustav Klimt: Margaret "Gretl" Stonborough-Wittgenstein. Stonborough-Wittgenstein, a member of the prominent and wealthy Viennese Wittgenstein family, was a sister of the philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein and the pianist Paul Wittgenstein. She was the subject of a portrait painted for her wedding by the artist Gustav Klimt (Stonborough-Wittgenstein and other members of the Wittgenstein family were among Klimt's most important patrons), which was sold in 1960 by her son Thomas and may now be seen in the Neue Pinakothek gallery in Munich. Aside: The painting appears briefly behind Ava, an AI robot, in the film Ex Machina (a film that is an excellent exploration of artificial intelligence, the nature of consciousness, and passing a Turing Test).
 Painting by Henri Matisse: Woman with a Hat (La femme au chapeau) depicts Matisse's wife, Amelie. It was painted in 1905 and exhibited at the Salon d'Automne during the fall of the same year, along with works by André Derain, Maurice de Vlaminck and several other artists known as "Fauves". Woman with a Hat was at the center of the controversy that led to the term Fauvism. It was also a painting that marked a stylistic shift in the work of Matisse from the Divisionist brushstrokes of his earlier work to a more expressive style. Its loose brushwork and "unfinished" quality shocking viewers as much as its vivid, non-naturalistic colors. Although the Fauve works on display were condemned by many — "A pot of paint has been flung in the face of the public", declared the critic Camille Mauclair — they also gained some favorable attention. The painting that was singled out for attacks was Matisse's Woman with a Hat.
Painting by Henri Matisse: Woman with a Hat (La femme au chapeau) depicts Matisse's wife, Amelie. It was painted in 1905 and exhibited at the Salon d'Automne during the fall of the same year, along with works by André Derain, Maurice de Vlaminck and several other artists known as "Fauves". Woman with a Hat was at the center of the controversy that led to the term Fauvism. It was also a painting that marked a stylistic shift in the work of Matisse from the Divisionist brushstrokes of his earlier work to a more expressive style. Its loose brushwork and "unfinished" quality shocking viewers as much as its vivid, non-naturalistic colors. Although the Fauve works on display were condemned by many — "A pot of paint has been flung in the face of the public", declared the critic Camille Mauclair — they also gained some favorable attention. The painting that was singled out for attacks was Matisse's Woman with a Hat.
(no entry for this year)
1906
 Upton Sinclair publishes The Jungle.
Upton Sinclair publishes The Jungle.
 painting by Henri Matisse: Le bonheur de vivre (The Joy of Life) is (along with Picasso's Les Demoiselles d'Avignon) regarded as one of the pillars of early modernism. The monumental canvas was first exhibited at the Salon des Indépendants of 1906, where its cadmium colors and spatial distortions caused a public expression of protest and outrage. "The work is known to have invigorated fellow artists, especially Pablo Picasso, who, in an effort to outdo Matisse in terms of shock value, immediately began work on his watershed Les Demoiselles D'Avignon," writes Martha Lucy, associate curator at the Barnes Foundation.
painting by Henri Matisse: Le bonheur de vivre (The Joy of Life) is (along with Picasso's Les Demoiselles d'Avignon) regarded as one of the pillars of early modernism. The monumental canvas was first exhibited at the Salon des Indépendants of 1906, where its cadmium colors and spatial distortions caused a public expression of protest and outrage. "The work is known to have invigorated fellow artists, especially Pablo Picasso, who, in an effort to outdo Matisse in terms of shock value, immediately began work on his watershed Les Demoiselles D'Avignon," writes Martha Lucy, associate curator at the Barnes Foundation.
(no entry for this year)
1907
Kenneth Grahame publishes The Wind in the Willows.
 Painting by Gustav Klimt : The Kiss (Lovers) was painted by the Austrian Symbolist painter Gustav Klimt between 1907 and 1908, the highpoint of his "Golden Period", when he painted a number of works in a similar gilded style. A perfect square, the canvas depicts a couple embracing, their bodies entwined in elaborate robes decorated in a style influenced by both linear constructs of the contemporary Art Nouveau style and the organic forms of the earlier Arts and Crafts movement. The work is composed of oil paint with applied layers of gold leaf, an aspect that gives it its strikingly modern, yet evocative appearance. The painting is now in the sterreichische Galerie Belvedere museum in the Belvedere palace, Vienna, and is widely considered a masterpiece of the early modern period. It is a symbol of Vienna Jugendstil Viennese Art Nouveau and is considered Klimt's most popular work
Painting by Gustav Klimt : The Kiss (Lovers) was painted by the Austrian Symbolist painter Gustav Klimt between 1907 and 1908, the highpoint of his "Golden Period", when he painted a number of works in a similar gilded style. A perfect square, the canvas depicts a couple embracing, their bodies entwined in elaborate robes decorated in a style influenced by both linear constructs of the contemporary Art Nouveau style and the organic forms of the earlier Arts and Crafts movement. The work is composed of oil paint with applied layers of gold leaf, an aspect that gives it its strikingly modern, yet evocative appearance. The painting is now in the sterreichische Galerie Belvedere museum in the Belvedere palace, Vienna, and is widely considered a masterpiece of the early modern period. It is a symbol of Vienna Jugendstil Viennese Art Nouveau and is considered Klimt's most popular work
 Painting by Gustav Klimt: Portrait of Adele Bloch-Bauer I (also called The Lady in Gold or The Woman in Gold) was completed between 1903 and 1907. The portrait was commissioned by the sitter's husband, Ferdinand Bloch-Bauer, a Jewish banker and sugar producer. It is the final and most fully representative work of Klimt's golden phase. The portrait was the first of two depictions of Adele by Klimt — the second was completed in 1912; these were two of several works by the artist that the family owned. Adele died in 1925; her will asked that the artworks by Klimt were to be left to the Österreichische Galerie Belvedere, although these belonged to Ferdinand, not her.
Painting by Gustav Klimt: Portrait of Adele Bloch-Bauer I (also called The Lady in Gold or The Woman in Gold) was completed between 1903 and 1907. The portrait was commissioned by the sitter's husband, Ferdinand Bloch-Bauer, a Jewish banker and sugar producer. It is the final and most fully representative work of Klimt's golden phase. The portrait was the first of two depictions of Adele by Klimt — the second was completed in 1912; these were two of several works by the artist that the family owned. Adele died in 1925; her will asked that the artworks by Klimt were to be left to the Österreichische Galerie Belvedere, although these belonged to Ferdinand, not her.
 Painting by Ivan Grohar: The Sower (Slovene: Sejalec), is an image of a peasant sowing seeds on a ploughed field in an early and foggy morning. A hayrack, typical of the Slovene landscape, stands in the back, and even farther, the rocks of the small hill Kamnitnik near Škofja Loka. It has been a metaphor for the 19th-century myth of Slovenes as a vigorous nation in front of an unclear destiny, a symbol for the Slovene nation that sows in order that it could harvest, and a depiction of human interrelatedness with the nature. It is also a reflection of the context of Slovene transition from a rural to an urban culture. It has become one of the most characteristic and established Slovene creations in visual arts.
Painting by Ivan Grohar: The Sower (Slovene: Sejalec), is an image of a peasant sowing seeds on a ploughed field in an early and foggy morning. A hayrack, typical of the Slovene landscape, stands in the back, and even farther, the rocks of the small hill Kamnitnik near Škofja Loka. It has been a metaphor for the 19th-century myth of Slovenes as a vigorous nation in front of an unclear destiny, a symbol for the Slovene nation that sows in order that it could harvest, and a depiction of human interrelatedness with the nature. It is also a reflection of the context of Slovene transition from a rural to an urban culture. It has become one of the most characteristic and established Slovene creations in visual arts.
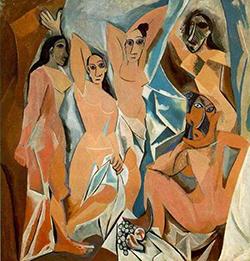 Painting by Pablo Picasso: Les Demoiselles d'Avignon (The Young Ladies of Avignon, and originally titled The Brothel of Avignon) portrays five nude female prostitutes from a brothel on Carrer d'Avinyó (Avinyó Street) in Barcelona. Each figure is depicted in a disconcerting confrontational manner and none are conventionally feminine. In this adaptation of Primitivism and abandonment of perspective in favor of a flat, two-dimensional picture plane, Picasso makes a radical departure from traditional European painting. This proto-Cubist work is widely considered to be seminal in the early development of both Cubism and Modern art. Les Demoiselles was revolutionary and controversial, and led to widespread anger and disagreement, even amongst the painter's closest associates and friends. Matisse considered the work something of a bad joke, yet indirectly reacted to it in his 1908 Bathers with a Turtle. Braque too initially disliked the painting, yet perhaps more than anyone else, studied the work in great detail. And effectively, his subsequent friendship and collaboration with Picasso led to the Cubist revolution
Painting by Pablo Picasso: Les Demoiselles d'Avignon (The Young Ladies of Avignon, and originally titled The Brothel of Avignon) portrays five nude female prostitutes from a brothel on Carrer d'Avinyó (Avinyó Street) in Barcelona. Each figure is depicted in a disconcerting confrontational manner and none are conventionally feminine. In this adaptation of Primitivism and abandonment of perspective in favor of a flat, two-dimensional picture plane, Picasso makes a radical departure from traditional European painting. This proto-Cubist work is widely considered to be seminal in the early development of both Cubism and Modern art. Les Demoiselles was revolutionary and controversial, and led to widespread anger and disagreement, even amongst the painter's closest associates and friends. Matisse considered the work something of a bad joke, yet indirectly reacted to it in his 1908 Bathers with a Turtle. Braque too initially disliked the painting, yet perhaps more than anyone else, studied the work in great detail. And effectively, his subsequent friendship and collaboration with Picasso led to the Cubist revolution
Henri Matisse coins the term "Cubism" — the first Cubist exhibition opens in Paris.
 Sculpture by Constantin Brâncusi: The Kiss is an early example of his proto-cubist style of non-literal representation. This plaster was exhibited at the 1913 Armory Show and published in the Chicago Tribune, 25 March 1913. This early plaster sculpture is one of six casts that Brancusi made of the 1907–08 The Kiss. The original stone carving is in the Muzeul de Arta at Craiova, Romania. Brâncusi created many versions of The Kiss, further simplifying geometric forms and sparse objects in each version, tending each time further toward abstraction. His abstract style emphasizes simple geometrical lines that balance forms inherent in his materials with the symbolic allusions of representational art. Here, the shape of the original block of material is maintained.
Sculpture by Constantin Brâncusi: The Kiss is an early example of his proto-cubist style of non-literal representation. This plaster was exhibited at the 1913 Armory Show and published in the Chicago Tribune, 25 March 1913. This early plaster sculpture is one of six casts that Brancusi made of the 1907–08 The Kiss. The original stone carving is in the Muzeul de Arta at Craiova, Romania. Brâncusi created many versions of The Kiss, further simplifying geometric forms and sparse objects in each version, tending each time further toward abstraction. His abstract style emphasizes simple geometrical lines that balance forms inherent in his materials with the symbolic allusions of representational art. Here, the shape of the original block of material is maintained.
(no entry for this year)
1908
 Painting by Georges Braque: Houses at l'Estaque (French: Maisons à l'Estaque) is considered either an important Proto-Cubist landscape or the first Cubist landscape. The painting prompted art critic Louis Vauxcelles to mock it as being composed of cubes which led to the name of the movement. This painting by Braque was refused at the Salon d'Automne in 1908. Louis Vauxcelles recounted how Matisse told him at the time, "Braque has just sent in [to the 1908 Salon d'Automne] a painting made of little cubes". The critic Charles Morice relayed Matisse's words and spoke of Braque's little cubes. The motif of the viaduct at l'Estaque had inspired Braque to produce three paintings marked by the simplification of form and deconstruction of perspective. Six landscapes painted at L'Estaque signed Georges Braque were presented to the Jury of the Salon d'Automne: Guérin, Marquet, Rouault and Matisse rejected Braque's entire submission. Guérin and Marquet elected to keep two in play. Braque withdrew the two in protest, placing the blame on Matisse.
Painting by Georges Braque: Houses at l'Estaque (French: Maisons à l'Estaque) is considered either an important Proto-Cubist landscape or the first Cubist landscape. The painting prompted art critic Louis Vauxcelles to mock it as being composed of cubes which led to the name of the movement. This painting by Braque was refused at the Salon d'Automne in 1908. Louis Vauxcelles recounted how Matisse told him at the time, "Braque has just sent in [to the 1908 Salon d'Automne] a painting made of little cubes". The critic Charles Morice relayed Matisse's words and spoke of Braque's little cubes. The motif of the viaduct at l'Estaque had inspired Braque to produce three paintings marked by the simplification of form and deconstruction of perspective. Six landscapes painted at L'Estaque signed Georges Braque were presented to the Jury of the Salon d'Automne: Guérin, Marquet, Rouault and Matisse rejected Braque's entire submission. Guérin and Marquet elected to keep two in play. Braque withdrew the two in protest, placing the blame on Matisse.
(no entry for this year)
1909
 Painting by Henri Matisse: Dance (La Danse). The title refers to either of two related paintings made between 1909 and 1910. The first, preliminary version is Matisse's study for the second version. The composition or arrangement of dancing figures is reminiscent of Blake's watercolour "Oberon, Titania and Puck with fairies dancing" from 1786.
Painting by Henri Matisse: Dance (La Danse). The title refers to either of two related paintings made between 1909 and 1910. The first, preliminary version is Matisse's study for the second version. The composition or arrangement of dancing figures is reminiscent of Blake's watercolour "Oberon, Titania and Puck with fairies dancing" from 1786.
ESP Quick Facts
ESP Origins
In the early 1990's, Robert Robbins was a faculty member at Johns Hopkins, where he directed the informatics core of GDB — the human gene-mapping database of the international human genome project. To share papers with colleagues around the world, he set up a small paper-sharing section on his personal web page. This small project evolved into The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Support
In 1995, Robbins became the VP/IT of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, WA. Soon after arriving in Seattle, Robbins secured funding, through the ELSI component of the US Human Genome Project, to create the original ESP.ORG web site, with the formal goal of providing free, world-wide access to the literature of classical genetics.
ESP Rationale
Although the methods of molecular biology can seem almost magical to the uninitiated, the original techniques of classical genetics are readily appreciated by one and all: cross individuals that differ in some inherited trait, collect all of the progeny, score their attributes, and propose mechanisms to explain the patterns of inheritance observed.
ESP Goal
In reading the early works of classical genetics, one is drawn, almost inexorably, into ever more complex models, until molecular explanations begin to seem both necessary and natural. At that point, the tools for understanding genome research are at hand. Assisting readers reach this point was the original goal of The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Usage
Usage of the site grew rapidly and has remained high. Faculty began to use the site for their assigned readings. Other on-line publishers, ranging from The New York Times to Nature referenced ESP materials in their own publications. Nobel laureates (e.g., Joshua Lederberg) regularly used the site and even wrote to suggest changes and improvements.
ESP Content
When the site began, no journals were making their early content available in digital format. As a result, ESP was obliged to digitize classic literature before it could be made available. For many important papers — such as Mendel's original paper or the first genetic map — ESP had to produce entirely new typeset versions of the works, if they were to be available in a high-quality format.
ESP Help
Early support from the DOE component of the Human Genome Project was critically important for getting the ESP project on a firm foundation. Since that funding ended (nearly 20 years ago), the project has been operated as a purely volunteer effort. Anyone wishing to assist in these efforts should send an email to Robbins.
ESP Plans
With the development of methods for adding typeset side notes to PDF files, the ESP project now plans to add annotated versions of some classical papers to its holdings. We also plan to add new reference and pedagogical material. We have already started providing regularly updated, comprehensive bibliographies to the ESP.ORG site.
ESP Picks from Around the Web (updated 06 MAR 2017 )
Old Science

Weird Science

Treating Disease with Fecal Transplantation
Fossils of miniature humans (hobbits) discovered in Indonesia

Dinosaur tail, complete with feathers, found preserved in amber.
Astronomy

Mysterious fast radio burst (FRB) detected in the distant universe.