MENU
The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project: Providing access to classic scientific papers and other scholarly materials, since 1993. More About: ESP | OUR CONTENT | THIS WEBSITE | WHAT'S NEW | WHAT'S HOT
Comparative Timelines
The ESP Timeline (one of the site's most popular features) has been completely updated to allow the user to select (using the timeline controls above each column) different topics for the left and right sides of the display.
Select:
New Left Column
New Left Column
Dates
Decade
New Right Column
New Right Column
(no entry for this year)
1440
 Painting by Domenico di Bartolo: Care of the Sick, shows, with impressive detail, the interior layout of the hospital ward. Doctors and nurses are depicted assisting the patients, as well as carrying out other generous deeds. The fresco also depicts in the center foreground the washing of the patient's feet, directly inferring to the well-known image of Christ washing the feet of his disciples. Throughout the whole painting, Domenico vividly brings out the color of the costume and its well-crafted décor. Because of such imitation of a real location, Domenico is said to have followed the works of Vecchietta, where both artists pave the way into a whole new area of descriptive realism to the world of Sienese art. Other painters at the time such as Gentile da Fabriano and Pisanello might have depicted landscapes to be realistic or naturalistic, but they were consistently known to create images that came out of fantasy and creativity. It was therefore new to the art world for both Domenico and Vecchietta to produce images that seem to imitate a specific location. The frescoes by Domenico are also one of the first works done in Sienese art that includes visual clues for its viewers.
Painting by Domenico di Bartolo: Care of the Sick, shows, with impressive detail, the interior layout of the hospital ward. Doctors and nurses are depicted assisting the patients, as well as carrying out other generous deeds. The fresco also depicts in the center foreground the washing of the patient's feet, directly inferring to the well-known image of Christ washing the feet of his disciples. Throughout the whole painting, Domenico vividly brings out the color of the costume and its well-crafted décor. Because of such imitation of a real location, Domenico is said to have followed the works of Vecchietta, where both artists pave the way into a whole new area of descriptive realism to the world of Sienese art. Other painters at the time such as Gentile da Fabriano and Pisanello might have depicted landscapes to be realistic or naturalistic, but they were consistently known to create images that came out of fantasy and creativity. It was therefore new to the art world for both Domenico and Vecchietta to produce images that seem to imitate a specific location. The frescoes by Domenico are also one of the first works done in Sienese art that includes visual clues for its viewers.
(no entry for this year)
1441
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1442
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1443
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1444
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1446
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1447
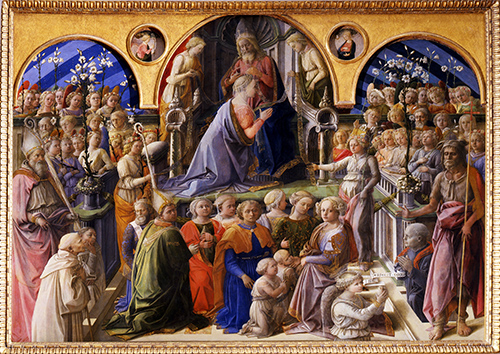 Painting by Filippo Lippi: Coronation of the Virgin, now in the Uffizi, Florence. Francesco Maringhi, procuratore of the church of Sant'Ambrogio, left money after his death in 1441 for a new painting at the high altar of the church. Bills of the payments for the work until 1447 have been preserved. In the late 1430s, brother Filippo Lippi had left the convent of the Carmine convent to open an artist workshop of his own; however, having no money enough to pay assistants and apprentices, he worked alone with two usual collaborators, Fra Carnevale and Fra Diamante, along with an unknown "Piero di Lorenzo dipintore". For the Coronation of the Virgin, however, Lippi had to call in a total of six external painters, who were responsible also for the gilded frame, now lost. Originally the work had a predella, also lost, with the exception of a small panel with a Miracle of Saint Ambrose, now in the Berlin State Museums. The work was immediately admired and was copied by numerous painters. It remained in Sant'Ambrogio until 1810, when it was stolen. Later it was sold to the Galleria dell'Accademia, from which it was transferred to the Galleria degli Uffizi in Florence.
Painting by Filippo Lippi: Coronation of the Virgin, now in the Uffizi, Florence. Francesco Maringhi, procuratore of the church of Sant'Ambrogio, left money after his death in 1441 for a new painting at the high altar of the church. Bills of the payments for the work until 1447 have been preserved. In the late 1430s, brother Filippo Lippi had left the convent of the Carmine convent to open an artist workshop of his own; however, having no money enough to pay assistants and apprentices, he worked alone with two usual collaborators, Fra Carnevale and Fra Diamante, along with an unknown "Piero di Lorenzo dipintore". For the Coronation of the Virgin, however, Lippi had to call in a total of six external painters, who were responsible also for the gilded frame, now lost. Originally the work had a predella, also lost, with the exception of a small panel with a Miracle of Saint Ambrose, now in the Berlin State Museums. The work was immediately admired and was copied by numerous painters. It remained in Sant'Ambrogio until 1810, when it was stolen. Later it was sold to the Galleria dell'Accademia, from which it was transferred to the Galleria degli Uffizi in Florence.
(no entry for this year)
1448
(no entry for this year)
(no entry for this year)
1449
 Painting by Filippo Lippi: The Annunciation, a tempera on panel painting, dating to c. 1449–1459, in the collection of the National Gallery, London. It is a pendant to Lippi's Seven Saints, also in the National Gallery. The lunettes were commissioned as part of the decoration of the Palazzo Medici in Florence, where they were likely placed above a door or a bed. There is general agreement on Lippi's authorship of the panels, but their dating is less certain; they were produced some time between Lorenzo the Magnificent's birth in 1449 and the completion of the palace's furnishing in 1459. That their patron belonged to the Medici family is testified by the presence of Piero di Cosimo de' Medici's coat of arms (three feathers crossed by a ring with diamond and cartouche) at the base of the small column with a vase which divides the painting in two. The painting depicts the Annunciation of Mary with the archangel Gabriel (left) and Mary (right). God, whose hand can be seen at the lunette's top is blessing Mary through the dove symbolizing the Holy Ghost.
Painting by Filippo Lippi: The Annunciation, a tempera on panel painting, dating to c. 1449–1459, in the collection of the National Gallery, London. It is a pendant to Lippi's Seven Saints, also in the National Gallery. The lunettes were commissioned as part of the decoration of the Palazzo Medici in Florence, where they were likely placed above a door or a bed. There is general agreement on Lippi's authorship of the panels, but their dating is less certain; they were produced some time between Lorenzo the Magnificent's birth in 1449 and the completion of the palace's furnishing in 1459. That their patron belonged to the Medici family is testified by the presence of Piero di Cosimo de' Medici's coat of arms (three feathers crossed by a ring with diamond and cartouche) at the base of the small column with a vase which divides the painting in two. The painting depicts the Annunciation of Mary with the archangel Gabriel (left) and Mary (right). God, whose hand can be seen at the lunette's top is blessing Mary through the dove symbolizing the Holy Ghost.
ESP Quick Facts
ESP Origins
In the early 1990's, Robert Robbins was a faculty member at Johns Hopkins, where he directed the informatics core of GDB — the human gene-mapping database of the international human genome project. To share papers with colleagues around the world, he set up a small paper-sharing section on his personal web page. This small project evolved into The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Support
In 1995, Robbins became the VP/IT of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, WA. Soon after arriving in Seattle, Robbins secured funding, through the ELSI component of the US Human Genome Project, to create the original ESP.ORG web site, with the formal goal of providing free, world-wide access to the literature of classical genetics.
ESP Rationale
Although the methods of molecular biology can seem almost magical to the uninitiated, the original techniques of classical genetics are readily appreciated by one and all: cross individuals that differ in some inherited trait, collect all of the progeny, score their attributes, and propose mechanisms to explain the patterns of inheritance observed.
ESP Goal
In reading the early works of classical genetics, one is drawn, almost inexorably, into ever more complex models, until molecular explanations begin to seem both necessary and natural. At that point, the tools for understanding genome research are at hand. Assisting readers reach this point was the original goal of The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Usage
Usage of the site grew rapidly and has remained high. Faculty began to use the site for their assigned readings. Other on-line publishers, ranging from The New York Times to Nature referenced ESP materials in their own publications. Nobel laureates (e.g., Joshua Lederberg) regularly used the site and even wrote to suggest changes and improvements.
ESP Content
When the site began, no journals were making their early content available in digital format. As a result, ESP was obliged to digitize classic literature before it could be made available. For many important papers — such as Mendel's original paper or the first genetic map — ESP had to produce entirely new typeset versions of the works, if they were to be available in a high-quality format.
ESP Help
Early support from the DOE component of the Human Genome Project was critically important for getting the ESP project on a firm foundation. Since that funding ended (nearly 20 years ago), the project has been operated as a purely volunteer effort. Anyone wishing to assist in these efforts should send an email to Robbins.
ESP Plans
With the development of methods for adding typeset side notes to PDF files, the ESP project now plans to add annotated versions of some classical papers to its holdings. We also plan to add new reference and pedagogical material. We have already started providing regularly updated, comprehensive bibliographies to the ESP.ORG site.
ESP Picks from Around the Web (updated 06 MAR 2017 )
Old Science

Weird Science

Treating Disease with Fecal Transplantation
Fossils of miniature humans (hobbits) discovered in Indonesia

Dinosaur tail, complete with feathers, found preserved in amber.
Astronomy

Mysterious fast radio burst (FRB) detected in the distant universe.