MENU
The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project: Providing access to classic scientific papers and other scholarly materials, since 1993. More About: ESP | OUR CONTENT | THIS WEBSITE | WHAT'S NEW | WHAT'S HOT
Comparative Timelines
The ESP Timeline (one of the site's most popular features) has been completely updated to allow the user to select (using the timeline controls above each column) different topics for the left and right sides of the display.
Select:
New Left Column
New Left Column
Dates
Decade
New Right Column
New Right Column
 Painting by Leonardo da Vinci: Lady with an Ermine, a portrait painting, in oils on a panel of walnut wood. Its subject is Cecilia Gallerani, a mistress of Ludovico Sforza ("Il Moro"), Duke of Milan; Leonardo was painter to the Sforza court in Milan at the time of its execution. It is the second of only four surviving portraits of women painted by Leonardo, the others being Ginevra de' Benci, La Belle Ferronnière and the Mona Lisa. Lady with an Ermine is now housed at the Czartoryski Museum in Kraków, and is one of Poland's national treasures.
Painting by Leonardo da Vinci: Lady with an Ermine, a portrait painting, in oils on a panel of walnut wood. Its subject is Cecilia Gallerani, a mistress of Ludovico Sforza ("Il Moro"), Duke of Milan; Leonardo was painter to the Sforza court in Milan at the time of its execution. It is the second of only four surviving portraits of women painted by Leonardo, the others being Ginevra de' Benci, La Belle Ferronnière and the Mona Lisa. Lady with an Ermine is now housed at the Czartoryski Museum in Kraków, and is one of Poland's national treasures.
 Painting by Cima da Conegliano: The Sacred Conversation
Painting by Cima da Conegliano: The Sacred Conversation
 Painting by Domenico Ghirlandaio: An Old Man and his Grandson, a tempera painting. One of Ghirlandaio's best-known works, it is considered notable for its emotional poignancy. Its realism has been described as unique among the portraits of the Quattrocento. The picture portrays an older man in a red robe, embracing a young child who is also wearing red. They sit in an interior, illuminated against a darkened wall. Behind them at right is a window through which can be seen a generalized landscape, its uneven terrain and winding roads typical of Ghirlandaio's backgrounds. Although the man's fur-lined robe and cappuccio and the boy's elegant doublet and cap indicate a noble heritage, and despite the traditional assumption that the subjects are grandfather and grandson, their identities are unknown.
Painting by Domenico Ghirlandaio: An Old Man and his Grandson, a tempera painting. One of Ghirlandaio's best-known works, it is considered notable for its emotional poignancy. Its realism has been described as unique among the portraits of the Quattrocento. The picture portrays an older man in a red robe, embracing a young child who is also wearing red. They sit in an interior, illuminated against a darkened wall. Behind them at right is a window through which can be seen a generalized landscape, its uneven terrain and winding roads typical of Ghirlandaio's backgrounds. Although the man's fur-lined robe and cappuccio and the boy's elegant doublet and cap indicate a noble heritage, and despite the traditional assumption that the subjects are grandfather and grandson, their identities are unknown.
 Painting by Leonardo da Vinci: Madonna Litta, a late 15th-century painting, by Leonardo da Vinci, in the Hermitage Museum, Saint Petersburg. It depicts the Virgin Mary breastfeeding the Christ child, a devotional subject known as the Madonna lactans. The figures are set in a dark interior with two arched openings, as in Leonardo's earlier Madonna of the Carnation, and a mountainous landscape in aerial perspective can be seen beyond. In his left hand Christ holds a goldfinch, which is symbolic of his future Passion. Scholarly opinion is divided on the work's attribution, with some believing it to be the work of a pupil of Leonardo such as Giovanni Antonio Boltraffio or Marco d'Oggiono; the Hermitage Museum, however, considers the painting to be an autograph work by Leonardo. The painting takes its name from the House of Litta, a Milanese noble family in whose collection it was for much of the nineteenth century.
Painting by Leonardo da Vinci: Madonna Litta, a late 15th-century painting, by Leonardo da Vinci, in the Hermitage Museum, Saint Petersburg. It depicts the Virgin Mary breastfeeding the Christ child, a devotional subject known as the Madonna lactans. The figures are set in a dark interior with two arched openings, as in Leonardo's earlier Madonna of the Carnation, and a mountainous landscape in aerial perspective can be seen beyond. In his left hand Christ holds a goldfinch, which is symbolic of his future Passion. Scholarly opinion is divided on the work's attribution, with some believing it to be the work of a pupil of Leonardo such as Giovanni Antonio Boltraffio or Marco d'Oggiono; the Hermitage Museum, however, considers the painting to be an autograph work by Leonardo. The painting takes its name from the House of Litta, a Milanese noble family in whose collection it was for much of the nineteenth century.
Leonardo da Vinci offers an explanation for capillary action — the ability of rise up in a narrow tube.
1490
(no entry for this year)
 Sculpture by Michelangelo: Madonna of the Stairs, a relief sculpture in the Casa Buonarroti, Florence. It was sculpted around 1490–91, when Michelangelo was about fifteen. This and the Battle of the Centaurs were Michelangelo's first two sculptures. The first reference to the Madonna of the Stairs as a work by Michelangelo was in the 1568 edition of Giorgio Vasari's Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculptors, and Architects. The sculpture is exhibited at the Casa Buonarroti in Florence, Italy.
Sculpture by Michelangelo: Madonna of the Stairs, a relief sculpture in the Casa Buonarroti, Florence. It was sculpted around 1490–91, when Michelangelo was about fifteen. This and the Battle of the Centaurs were Michelangelo's first two sculptures. The first reference to the Madonna of the Stairs as a work by Michelangelo was in the 1568 edition of Giorgio Vasari's Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculptors, and Architects. The sculpture is exhibited at the Casa Buonarroti in Florence, Italy.
1491
King Charles VIII of France invades Brittany and forces 14-year-old Ann of Brittany to marry him, adding Brittany to French territory.
 Christopher Columbus left Castile in August 1492 with three ships and made landfall in the Americas on 12 October, ending the period of human habitation in the Americas now referred to as the pre-Columbian era. His landing place was an island in the Bahamas, known by its native inhabitants as Guanahani. He then visited the islands now known as Cuba and Hispaniola, establishing a colony in what is now Haiti. Columbus returned to Castile in early 1493, with captured natives. Word of his voyage soon spread throughout Europe.
Christopher Columbus left Castile in August 1492 with three ships and made landfall in the Americas on 12 October, ending the period of human habitation in the Americas now referred to as the pre-Columbian era. His landing place was an island in the Bahamas, known by its native inhabitants as Guanahani. He then visited the islands now known as Cuba and Hispaniola, establishing a colony in what is now Haiti. Columbus returned to Castile in early 1493, with captured natives. Word of his voyage soon spread throughout Europe.
 Sculpture by Michelangelo: Battle of the Centaurs, a relief created around 1492. It was the last work Michelangelo created while under the patronage of Lorenzo de' Medici, who died shortly after its completion. Inspired by a classical relief created by Bertoldo di Giovanni, the marble sculpture represents the mythic battle between the Lapiths and the Centaurs. A popular subject of art in ancient Greece, the story was suggested to Michelangelo by the classical scholar and poet Poliziano. The sculpture is exhibited in the Casa Buonarroti in Florence, Italy. Michelangelo, at 16, was working under the patronage of Lorenzo de' Medici when he sculpted the Battle of the Centaurs, although the work was not commissioned but created for himself. The work reflected what was then a current fashion for reproducing ancient themes.
Sculpture by Michelangelo: Battle of the Centaurs, a relief created around 1492. It was the last work Michelangelo created while under the patronage of Lorenzo de' Medici, who died shortly after its completion. Inspired by a classical relief created by Bertoldo di Giovanni, the marble sculpture represents the mythic battle between the Lapiths and the Centaurs. A popular subject of art in ancient Greece, the story was suggested to Michelangelo by the classical scholar and poet Poliziano. The sculpture is exhibited in the Casa Buonarroti in Florence, Italy. Michelangelo, at 16, was working under the patronage of Lorenzo de' Medici when he sculpted the Battle of the Centaurs, although the work was not commissioned but created for himself. The work reflected what was then a current fashion for reproducing ancient themes.
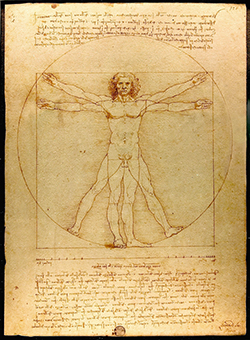 Drawing by Leonardo da Vinci: Vitruvian Man. Inspired by the writings of the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius, the drawing depicts a nude man in two superimposed positions with his arms and legs apart and inscribed in both a circle and square. It was described by the art historian Carmen C. Bambach as "justly ranked among the all-time iconic images of Western civilization". Although not the only known drawing of a man inspired by the writings of Vitruvius, the work is a unique synthesis of artistic and scientific ideals and often considered an archetypal representation of the High Renaissance. The drawing represents Leonardo's conception of ideal body proportions, originally derived from Vitruvius but influenced by his own measurements, the drawings of his contemporaries, and the De pictura treatise by Leon Battista Alberti. Leonardo produced the Vitruvian Man in Milan and the work was probably passed to his student Francesco Melzi.
Drawing by Leonardo da Vinci: Vitruvian Man. Inspired by the writings of the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius, the drawing depicts a nude man in two superimposed positions with his arms and legs apart and inscribed in both a circle and square. It was described by the art historian Carmen C. Bambach as "justly ranked among the all-time iconic images of Western civilization". Although not the only known drawing of a man inspired by the writings of Vitruvius, the work is a unique synthesis of artistic and scientific ideals and often considered an archetypal representation of the High Renaissance. The drawing represents Leonardo's conception of ideal body proportions, originally derived from Vitruvius but influenced by his own measurements, the drawings of his contemporaries, and the De pictura treatise by Leon Battista Alberti. Leonardo produced the Vitruvian Man in Milan and the work was probably passed to his student Francesco Melzi.
 Italian explorer Christopher Columbus observes that Native Americans use tobacco as a medicinal herb. Columbus acquires some dried tobacco leaves from the Natives, personally tests the leaves for efficacy, and then (as a satisfied customer) transports samples back to Europe.
Italian explorer Christopher Columbus observes that Native Americans use tobacco as a medicinal herb. Columbus acquires some dried tobacco leaves from the Natives, personally tests the leaves for efficacy, and then (as a satisfied customer) transports samples back to Europe.
Leonardo da Vinci is the first the theorize seriously about flying machines.
Tobacco plant and smoking first introduced in Europe. Human health will be changed for centuries.
1492
Spain's monarchs, Ferdinand and Isabella, do their part in a war against Islam — they annex Granada. Also they give Jews three months to convert to Christianity if they are to avoid banishment from the country. And the voyage that the monarchy is paying for, led by Christopher Columbus, sets sail for China by going westward.
 Painting by Albrecht Dürer: Christ as the Man of Sorrows. Bearing the marks of martyrdom and holding the instruments used to scourge him in his hands, a pensive, exhausted man crouches before us and looks straight at us, questioningly. This is an unusual mixture of a concrete moment in time and a summary of the entire Passion of Jesus. With the living figure of Christ and the expressive look on his face, this work testifies to the perceptiveness of the young Dürer. By inviting believers in a special way to immerse themselves compassionately in the man's suffering, the small format painting shows itself to be an exceptional devotional picture.
Painting by Albrecht Dürer: Christ as the Man of Sorrows. Bearing the marks of martyrdom and holding the instruments used to scourge him in his hands, a pensive, exhausted man crouches before us and looks straight at us, questioningly. This is an unusual mixture of a concrete moment in time and a summary of the entire Passion of Jesus. With the living figure of Christ and the expressive look on his face, this work testifies to the perceptiveness of the young Dürer. By inviting believers in a special way to immerse themselves compassionately in the man's suffering, the small format painting shows itself to be an exceptional devotional picture.
 Painting by Hieronymus Bosch: The Hermit Saints, a religious oil on panel painting displayed as a triptych. The entirety of the triptych painting measures 86 by 60 centimetres (34 in × 24 in). This artwork is currently being housed at the Gallerie dell'Accademia, Venice. Saints are a common theme in Bosch's artwork; for him, they are a reference to the living and also to suffering against what was considered sinful. Likewise, there is often the portrayal of brutality and agony that far outweighs the beauty in Bosch's work since he uses saints as a moral paradigm of the artist's time. He represents them as those who are most faithful in their beliefs.
Painting by Hieronymus Bosch: The Hermit Saints, a religious oil on panel painting displayed as a triptych. The entirety of the triptych painting measures 86 by 60 centimetres (34 in × 24 in). This artwork is currently being housed at the Gallerie dell'Accademia, Venice. Saints are a common theme in Bosch's artwork; for him, they are a reference to the living and also to suffering against what was considered sinful. Likewise, there is often the portrayal of brutality and agony that far outweighs the beauty in Bosch's work since he uses saints as a moral paradigm of the artist's time. He represents them as those who are most faithful in their beliefs.
1493
(no entry for this year)
 Painting by Leonardo da Vinci: La Belle Ferronnière,a portrait painting of a lady. It is also known as Portrait of an Unknown Woman. The painting's title, applied as early as the seventeenth century, identifying the sitter as the wife or daughter of an ironmonger (a ferronnier), was said to be discreetly alluding to a reputed mistress of Francis I of France, married to a certain Le Ferron. Later she was tentatively identified as Lucretia Crivelli, a married lady-in-waiting to Duchess Beatrice of Milan, who became another of the Duke's mistresses. Although the model of the painting La Belle Ferronnière is still shrouded in mystery, the landmark exhibition "Leonardo Da Vinci: Painter at the Court of Milan" (National Gallery, London, 9 Nov. 2011 – 5 Feb. 2012) listed the portrait as possibly depicting Beatrice d'Este, wife of Ludovico Sforza. This challenges an earlier identification of the sitter as Lucrezia Crivelli, a mistress of Ludovico. However, Ferronni&egrare could be a reference to Beatrice Sforza's birthplace, the Duchy of Ferrara.
Painting by Leonardo da Vinci: La Belle Ferronnière,a portrait painting of a lady. It is also known as Portrait of an Unknown Woman. The painting's title, applied as early as the seventeenth century, identifying the sitter as the wife or daughter of an ironmonger (a ferronnier), was said to be discreetly alluding to a reputed mistress of Francis I of France, married to a certain Le Ferron. Later she was tentatively identified as Lucretia Crivelli, a married lady-in-waiting to Duchess Beatrice of Milan, who became another of the Duke's mistresses. Although the model of the painting La Belle Ferronnière is still shrouded in mystery, the landmark exhibition "Leonardo Da Vinci: Painter at the Court of Milan" (National Gallery, London, 9 Nov. 2011 – 5 Feb. 2012) listed the portrait as possibly depicting Beatrice d'Este, wife of Ludovico Sforza. This challenges an earlier identification of the sitter as Lucrezia Crivelli, a mistress of Ludovico. However, Ferronni&egrare could be a reference to Beatrice Sforza's birthplace, the Duchy of Ferrara.
Following heavy snowfall in Florence, the Italian sculptor Michelangelo was commissioned by the Medicis to build a snowman.
 Summa de arithmetica, geometria, proportioni et proportionalita (Summary of arithmetic, geometry, proportions and proportionality) is a book on mathematics written by Luca Pacioli and first published in 1494. It contains a comprehensive summary of Renaissance mathematics, including practical arithmetic, basic algebra, basic geometry and accounting, written for use as a textbook and reference work. Written in vernacular Italian, the Summa is the first printed work on algebra, and it contains the first published description of the double-entry bookkeeping system. It set a new standard for writing and argumentation about algebra, and its impact upon the subsequent development and standardization of professional accounting methods was so great that Pacioli is sometimes referred to as the "father of accounting".
Summa de arithmetica, geometria, proportioni et proportionalita (Summary of arithmetic, geometry, proportions and proportionality) is a book on mathematics written by Luca Pacioli and first published in 1494. It contains a comprehensive summary of Renaissance mathematics, including practical arithmetic, basic algebra, basic geometry and accounting, written for use as a textbook and reference work. Written in vernacular Italian, the Summa is the first printed work on algebra, and it contains the first published description of the double-entry bookkeeping system. It set a new standard for writing and argumentation about algebra, and its impact upon the subsequent development and standardization of professional accounting methods was so great that Pacioli is sometimes referred to as the "father of accounting".
Whiskey invented in Scotland.
1494
Piero de Medici has ruled since the death of his father, Lorenzo, in 1492. He makes peace with the French, who have invaded Tuscany (in which Florence is located). A political rising drives him into exile. Florence is in anarchy. A Dominican priest, Savonarola, is anti-Renaissance. He is opposed to popular music, art and other worldliness.
 The Treaty of Tordesillas, signed in Tordesillas, Spain, on 7 June 1494, and ratified in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Kingdom of Portugal and the Crown of Castile, along a meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde islands, off the west coast of Africa. That line of demarcation was about halfway between Cape Verde (already Portuguese) and the islands visited by Christopher Columbus on his first voyage (claimed for Castile and León), named in the treaty as Cipangu and Antillia (Cuba and Hispaniola). The lands to the east would belong to Portugal and the lands to the west to Castile, modifying an earlier bull by Pope Alexander VI. The treaty was signed by Spain on 2 July 1494, and by Portugal on 5 September 1494. The other side of the world was divided a few decades later by the Treaty of Zaragoza, signed on 22 April 1529, which specified the antimeridian to the line of demarcation specified in the Treaty of Tordesillas. Portugal and Spain largely respected the treaties, while the indigenous peoples of the Americas did not acknowledge them.
The Treaty of Tordesillas, signed in Tordesillas, Spain, on 7 June 1494, and ratified in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Kingdom of Portugal and the Crown of Castile, along a meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde islands, off the west coast of Africa. That line of demarcation was about halfway between Cape Verde (already Portuguese) and the islands visited by Christopher Columbus on his first voyage (claimed for Castile and León), named in the treaty as Cipangu and Antillia (Cuba and Hispaniola). The lands to the east would belong to Portugal and the lands to the west to Castile, modifying an earlier bull by Pope Alexander VI. The treaty was signed by Spain on 2 July 1494, and by Portugal on 5 September 1494. The other side of the world was divided a few decades later by the Treaty of Zaragoza, signed on 22 April 1529, which specified the antimeridian to the line of demarcation specified in the Treaty of Tordesillas. Portugal and Spain largely respected the treaties, while the indigenous peoples of the Americas did not acknowledge them.
 Painting by Piero di Cosimo: The Death of Procris, A Satyr mourning over a Nymph are names given to an unsigned, undated panel painting in the National Gallery in London, United Kingdom, securely attributed to Piero di Cosimo (who never signed his works). Its date is uncertain, and its subject has been a matter of dispute. The name The Death of Procris (Italian: Morte di Procri) has been used since the 19th century, and is supposed to have been inspired by Ovid's tale of the death of Procris at the hands of her husband Cephalus, in Metamorphoses VII. Despite the uncertainty surrounding the subject matter, the painting, which shows a satyr mourning over the body of a young woman, has been one of the most popular works by Piero di Cosimo. Erwin Panofsky was mesmerized by the "strange lure emanating from the picture", and other commentators have admired its "hazy atmosphere of a waking dream".
Painting by Piero di Cosimo: The Death of Procris, A Satyr mourning over a Nymph are names given to an unsigned, undated panel painting in the National Gallery in London, United Kingdom, securely attributed to Piero di Cosimo (who never signed his works). Its date is uncertain, and its subject has been a matter of dispute. The name The Death of Procris (Italian: Morte di Procri) has been used since the 19th century, and is supposed to have been inspired by Ovid's tale of the death of Procris at the hands of her husband Cephalus, in Metamorphoses VII. Despite the uncertainty surrounding the subject matter, the painting, which shows a satyr mourning over the body of a young woman, has been one of the most popular works by Piero di Cosimo. Erwin Panofsky was mesmerized by the "strange lure emanating from the picture", and other commentators have admired its "hazy atmosphere of a waking dream".
 Scroll by Sesshū Tōyō: Haboku sansui, Broken Ink Landscape, a splashed-ink landscape painting on a hanging scroll. The ink wash painting is classified as a National Treasure of Japan and currently held by the Tokyo National Museum. Sesshū Tōyō was a Zen Buddhist monk and painter. The work is a development of suibokuga paintings made with Chinese ink (sumi), using dark and light shades on a silk or paper medium. The monochromatic style can result in artworks similar to calligraphy. In spite of its title, the work is not one of "broken ink" (haboku) but rather one of "splashed ink" (hatsuboku). In this style, the painter avoids strongly defined outlines, with shapes indicated by color washes in lighter and darker tones. The work slowly reveals itself to the viewer. Emerging from the undefined forms is the suggestion of misty mountains in the background. In the foreground are cliffs and bushes, and the triangular roofline and a sloping banner for a wine shop with vertical lines forming a fence. Below is indicated the flat surface of a body of water, with two people to the right in a rowing boat. The scroll measures 148.6 by 32.7 centimetres (58.5 in × 12.9 in). It bears a dedicatory inscription by the artist, dating it to the middle of the third month in the fourth year of the Meiō era (that is, April or May 1495), when Sesshū was aged 76.
Scroll by Sesshū Tōyō: Haboku sansui, Broken Ink Landscape, a splashed-ink landscape painting on a hanging scroll. The ink wash painting is classified as a National Treasure of Japan and currently held by the Tokyo National Museum. Sesshū Tōyō was a Zen Buddhist monk and painter. The work is a development of suibokuga paintings made with Chinese ink (sumi), using dark and light shades on a silk or paper medium. The monochromatic style can result in artworks similar to calligraphy. In spite of its title, the work is not one of "broken ink" (haboku) but rather one of "splashed ink" (hatsuboku). In this style, the painter avoids strongly defined outlines, with shapes indicated by color washes in lighter and darker tones. The work slowly reveals itself to the viewer. Emerging from the undefined forms is the suggestion of misty mountains in the background. In the foreground are cliffs and bushes, and the triangular roofline and a sloping banner for a wine shop with vertical lines forming a fence. Below is indicated the flat surface of a body of water, with two people to the right in a rowing boat. The scroll measures 148.6 by 32.7 centimetres (58.5 in × 12.9 in). It bears a dedicatory inscription by the artist, dating it to the middle of the third month in the fourth year of the Meiō era (that is, April or May 1495), when Sesshū was aged 76.
 Engraving by Albrecht Dürer: The Holy Family with the Dragonfly, also known as The Holy Family with the Mayfly, The Holy Family with the Locust, and The Holy Family with the Butterfly. It depicts both the Holy Family and the Holy Trinity, as the Virgin Mary sits on a bench holding Jesus with Joseph beside them, while God the Father and the Holy Ghost in the form of a dove look down from the clouds. In the lower right corner is an insect frequently identified as a dragonfly. However, Dürer may have intended it as a butterfly, a creature whose dramatically transformative life-cycle makes it a perfect symbol of resurrection and redemption. The abundance of beautifully-rendered textures in the richly detailed landscape show how early Dürer mastered the art of engraving.
Engraving by Albrecht Dürer: The Holy Family with the Dragonfly, also known as The Holy Family with the Mayfly, The Holy Family with the Locust, and The Holy Family with the Butterfly. It depicts both the Holy Family and the Holy Trinity, as the Virgin Mary sits on a bench holding Jesus with Joseph beside them, while God the Father and the Holy Ghost in the form of a dove look down from the clouds. In the lower right corner is an insect frequently identified as a dragonfly. However, Dürer may have intended it as a butterfly, a creature whose dramatically transformative life-cycle makes it a perfect symbol of resurrection and redemption. The abundance of beautifully-rendered textures in the richly detailed landscape show how early Dürer mastered the art of engraving.
French gunners begin using cast-iron cannonballs rather than stones.
1495
(no entry for this year)
 Painting by Vittore Carpaccio: Miracle of the Relic of the Cross at the Ponte di Rialto, also known as The Healing of the Madman, is a painting dating from c. 1496. It is now housed at the Gallerie dell'Accademia in Venice. The painting was commissioned for the Grand Hall of the Scuola Grande di San Giovanni Evangelista, the seat of the eponymous brotherhood in Venice. The subject of the paintings was to be the miracles of a fragment of the True Cross. The canvasses were all executed between 1496–1501. This painting shows the miracle of the healing of a madman through the relic of the Holy Cross, held by the Patriarch of Grado Francesco Querini, which took place in the Palazzo a San Silvestro on the Canal Grande, near the Rialto Bridge.
Painting by Vittore Carpaccio: Miracle of the Relic of the Cross at the Ponte di Rialto, also known as The Healing of the Madman, is a painting dating from c. 1496. It is now housed at the Gallerie dell'Accademia in Venice. The painting was commissioned for the Grand Hall of the Scuola Grande di San Giovanni Evangelista, the seat of the eponymous brotherhood in Venice. The subject of the paintings was to be the miracles of a fragment of the True Cross. The canvasses were all executed between 1496–1501. This painting shows the miracle of the healing of a madman through the relic of the Holy Cross, held by the Patriarch of Grado Francesco Querini, which took place in the Palazzo a San Silvestro on the Canal Grande, near the Rialto Bridge.
 Painting by Leonardo da Vinci: La Bella Principessa,also known as Portrait of Bianca Sforza, Young Girl in Profile in Renaissance Dress and Portrait of a Young Fiancée, is a portrait in colored chalks and ink, on vellum, of a young lady in fashionable costume and hairstyle of a Milanese of the 1490s. Some scholars have attributed it to Leonardo da Vinci but the attribution and the work's authenticity have been disputed. Supporters of the theory that it was by Leonardo have propositioned that Bianca Maria Sforza is the woman depicted in the drawing. Some of those who disagree with the attribution to Leonardo believe the portrait is by an early 19th-century German artist imitating the style of the Italian Renaissance, although radiocarbon dating tests show a much earlier date for the vellum. It has also been denounced as a forgery. The white lead has been dated to be at least 225 years old. The work sold for just under $22,000 at auction in 1998, and was bought by its current owner Peter Silverman in 2007. He has championed the attribution to Leonardo, supported by the analysis of academics Martin Kemp and Pascal Cotte.
Painting by Leonardo da Vinci: La Bella Principessa,also known as Portrait of Bianca Sforza, Young Girl in Profile in Renaissance Dress and Portrait of a Young Fiancée, is a portrait in colored chalks and ink, on vellum, of a young lady in fashionable costume and hairstyle of a Milanese of the 1490s. Some scholars have attributed it to Leonardo da Vinci but the attribution and the work's authenticity have been disputed. Supporters of the theory that it was by Leonardo have propositioned that Bianca Maria Sforza is the woman depicted in the drawing. Some of those who disagree with the attribution to Leonardo believe the portrait is by an early 19th-century German artist imitating the style of the Italian Renaissance, although radiocarbon dating tests show a much earlier date for the vellum. It has also been denounced as a forgery. The white lead has been dated to be at least 225 years old. The work sold for just under $22,000 at auction in 1998, and was bought by its current owner Peter Silverman in 2007. He has championed the attribution to Leonardo, supported by the analysis of academics Martin Kemp and Pascal Cotte.
 The bronze equestrian statue of Bartolomeo Colleoni designed by Andrea del Verrocchio and completed by Alessandro Leopardi is unveiled in Venice
The bronze equestrian statue of Bartolomeo Colleoni designed by Andrea del Verrocchio and completed by Alessandro Leopardi is unveiled in Venice
1496
(no entry for this year)
 Sculpture by Michelangelo: Bacchus. The statue is somewhat over life-size and represents Bacchus, the Roman god of wine, in a reeling pose suggestive of drunkenness. Commissioned by Raffaele Riario, a high-ranking Cardinal and collector of antique sculpture, it was rejected by him and was bought instead by Jacopo Galli, Riario's banker and a friend to Michelangelo. Together with the Pietà, the Bacchus is one of only two surviving sculptures from the artist's first period in Rome.
Sculpture by Michelangelo: Bacchus. The statue is somewhat over life-size and represents Bacchus, the Roman god of wine, in a reeling pose suggestive of drunkenness. Commissioned by Raffaele Riario, a high-ranking Cardinal and collector of antique sculpture, it was rejected by him and was bought instead by Jacopo Galli, Riario's banker and a friend to Michelangelo. Together with the Pietà, the Bacchus is one of only two surviving sculptures from the artist's first period in Rome.
 Engraving by Albrecht Dürer: The Four Naked Women, or The Four Witches. It is one of his earliest signed engravings and shows four exuberant nude women gathered conspiratorially in a circle in a confined interior setting, perhaps a bathhouse, which appears to have entrances from either side. Although the image is clearly erotic, a small horned demon in the left-hand portal, perhaps representing temptation, looks out and holds what may be a hunting object, engulfed in flames. The engraving has been subject to prolonged and significant scholarly analysis it remains enigmatic, and there is nothing in his writings to indicate his intent. There is no consensus as to its subject matter or its intended meaning, with art historians associating it with either witch hunting or figures from classical mythology. The women stand underneath a suspended globe or sphere and before an open stone window, which, given the human skull and thigh bone placed across from it, maybe a gateway to death, and that the women are engaged in some type of nefarious scheme, perhaps linked to the 1487 inquisition treatise Malleus Maleficarum. The alternative view is that the women represent Greek or Roman goddesses, perhaps Hecate, patroness of evil magic, poisonous plants, and ghosts, or her earthly counterpart Diana. Dürer's monogram "AD" appears on the centre of the floor. Numerous original prints exist, held at a number of major museums.
Engraving by Albrecht Dürer: The Four Naked Women, or The Four Witches. It is one of his earliest signed engravings and shows four exuberant nude women gathered conspiratorially in a circle in a confined interior setting, perhaps a bathhouse, which appears to have entrances from either side. Although the image is clearly erotic, a small horned demon in the left-hand portal, perhaps representing temptation, looks out and holds what may be a hunting object, engulfed in flames. The engraving has been subject to prolonged and significant scholarly analysis it remains enigmatic, and there is nothing in his writings to indicate his intent. There is no consensus as to its subject matter or its intended meaning, with art historians associating it with either witch hunting or figures from classical mythology. The women stand underneath a suspended globe or sphere and before an open stone window, which, given the human skull and thigh bone placed across from it, maybe a gateway to death, and that the women are engaged in some type of nefarious scheme, perhaps linked to the 1487 inquisition treatise Malleus Maleficarum. The alternative view is that the women represent Greek or Roman goddesses, perhaps Hecate, patroness of evil magic, poisonous plants, and ghosts, or her earthly counterpart Diana. Dürer's monogram "AD" appears on the centre of the floor. Numerous original prints exist, held at a number of major museums.
Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus records a star being occluded by the moon.
1497
Boys working under Savonarola collect from homes things associated with moral laxity: mirrors, cosmetics, pictures, books, fine dresses, the works of immoral poets. Savonarola has these burned. Renaissance art work is lost. Pope Alexander VI excommunicates Savonarola.
 Painting by Leonardo da Vinci: The Last Supper, a mural painting, dated to c. 1495–1498, housed in the refectory of the Convent of Santa Maria delle Grazie in Milan, Italy. The painting represents the scene of the Last Supper of Jesus with the Twelve Apostles, as it is told in the Gospel of John — specifically the moment after Jesus announces that one of his apostles will betray him. Its handling of space, mastery of perspective, treatment of motion and complex display of human emotion has made it one of the Western world's most recognizable paintings and among Leonardo's most celebrated works. Some commentators consider it pivotal in inaugurating the transition into what is now termed the High Renaissance. The painting is huge (roughly 15 feet × 30 feet) and covers the end wall of the refectory. To appreciate the size, one must see it in person.
Painting by Leonardo da Vinci: The Last Supper, a mural painting, dated to c. 1495–1498, housed in the refectory of the Convent of Santa Maria delle Grazie in Milan, Italy. The painting represents the scene of the Last Supper of Jesus with the Twelve Apostles, as it is told in the Gospel of John — specifically the moment after Jesus announces that one of his apostles will betray him. Its handling of space, mastery of perspective, treatment of motion and complex display of human emotion has made it one of the Western world's most recognizable paintings and among Leonardo's most celebrated works. Some commentators consider it pivotal in inaugurating the transition into what is now termed the High Renaissance. The painting is huge (roughly 15 feet × 30 feet) and covers the end wall of the refectory. To appreciate the size, one must see it in person.
 Painting by Albrecht Dürer: Self Portrait, the second of Albrecht Dürer's three painted self-portraits and was executed in oil on wood panel, after his first trip to Italy. In the depiction, Dürer elevates himself to the social position he believed suited to an artist of his ability. He presents himself in half length, under an arch, turned towards the viewer. He bears an arrogant expression, betraying the assured self-confidence of a young artist at the height of his ability. His presence dominates the pictorial space, from his hat, which almost reaches the top of the canvas, to his arm positioned on the lower ledge, where he rests his fingers enclosed in fine, rich gloves. Dürer is depicted in front of an open window before a flat landscape containing a lake and distant snow-capped mountains. The landscape may represent either the memory of his recent travels abroad or his inner mental state. Light spills from the window, falling along his head to highlight both his delicate skin tones and long blond hair. Dürer is dressed with effeminate grace in flamboyant, extravagant clothes showing the influence of Italian fashion. His low-necked shirt or chemise is of fine linen, gathered and trimmed with a band of gold braid or embroidery, and worn under an open-fronted doublet and a cloak tied over one shoulder. His white jacket has black lining under a pleated white shirt, the verticals of which match the horizontals of his headdress. His fingers are crossed, hidden inside silk gloves, an unusual pose for Dürer's early career; he always paid close attention in detailing the hands of his sitters, who are usually holding an object; examples include a pillow, rosary, sheet of paper and flower. Dürer is presented as almost seductive, with a rakish patterned hat placed over long, almost girlishly curled blond locks of hair under a draped pointed hat with a tassel. He looks out at the viewer with a cool ironic stare.
Painting by Albrecht Dürer: Self Portrait, the second of Albrecht Dürer's three painted self-portraits and was executed in oil on wood panel, after his first trip to Italy. In the depiction, Dürer elevates himself to the social position he believed suited to an artist of his ability. He presents himself in half length, under an arch, turned towards the viewer. He bears an arrogant expression, betraying the assured self-confidence of a young artist at the height of his ability. His presence dominates the pictorial space, from his hat, which almost reaches the top of the canvas, to his arm positioned on the lower ledge, where he rests his fingers enclosed in fine, rich gloves. Dürer is depicted in front of an open window before a flat landscape containing a lake and distant snow-capped mountains. The landscape may represent either the memory of his recent travels abroad or his inner mental state. Light spills from the window, falling along his head to highlight both his delicate skin tones and long blond hair. Dürer is dressed with effeminate grace in flamboyant, extravagant clothes showing the influence of Italian fashion. His low-necked shirt or chemise is of fine linen, gathered and trimmed with a band of gold braid or embroidery, and worn under an open-fronted doublet and a cloak tied over one shoulder. His white jacket has black lining under a pleated white shirt, the verticals of which match the horizontals of his headdress. His fingers are crossed, hidden inside silk gloves, an unusual pose for Dürer's early career; he always paid close attention in detailing the hands of his sitters, who are usually holding an object; examples include a pillow, rosary, sheet of paper and flower. Dürer is presented as almost seductive, with a rakish patterned hat placed over long, almost girlishly curled blond locks of hair under a draped pointed hat with a tassel. He looks out at the viewer with a cool ironic stare.
 Portuguese navigator Vasco de Gama sails around the Cape of Good Hope and crosses the Indian Ocean to reach India.
Portuguese navigator Vasco de Gama sails around the Cape of Good Hope and crosses the Indian Ocean to reach India.
1498
Savonarola is hanged. An enraged crowd burns Savonarola at the same spot where he ordered his bonfire.
 Drawing by Leonardo da Vinci: Portrait of Isabella d'Este,which was executed between 1499 and 1500. It depicts Isabella d'Este, Marchioness of Mantua. During the Italian Wars of 1499–1504, the French invaded Italy which caused Leonardo to flee from Milan to Mantua. There he had met Isabella, where she commissioned her portrait from him. Whether Leonardo completed the portrait is unknown. There is evidence through letters of the time that he held a fully completed painting of her, but they are vague in describing it. It is possible that the painting was lost to time or that it was, in fact, never completed at all. A version of the portrait in oils on canvas was found in a collection in Switzerland in 2015, but it has yet to be verified.
Drawing by Leonardo da Vinci: Portrait of Isabella d'Este,which was executed between 1499 and 1500. It depicts Isabella d'Este, Marchioness of Mantua. During the Italian Wars of 1499–1504, the French invaded Italy which caused Leonardo to flee from Milan to Mantua. There he had met Isabella, where she commissioned her portrait from him. Whether Leonardo completed the portrait is unknown. There is evidence through letters of the time that he held a fully completed painting of her, but they are vague in describing it. It is possible that the painting was lost to time or that it was, in fact, never completed at all. A version of the portrait in oils on canvas was found in a collection in Switzerland in 2015, but it has yet to be verified.
 Sculpture by Michelangelo: the Pietà, a Carrara marble sculpture of Jesus and Mary at Mount Golgotha representing the "Sixth Sorrow" of the Virgin Mary by Michelangelo Buonarroti, in Saint Peter's Basilica, Vatican City, for which it was made . It is a key work of Italian Renaissance sculpture and often taken as the start of the High Renaissance. The sculpture captures the moment when Jesus, taken down from the cross, is given to his mother Mary.
Sculpture by Michelangelo: the Pietà, a Carrara marble sculpture of Jesus and Mary at Mount Golgotha representing the "Sixth Sorrow" of the Virgin Mary by Michelangelo Buonarroti, in Saint Peter's Basilica, Vatican City, for which it was made . It is a key work of Italian Renaissance sculpture and often taken as the start of the High Renaissance. The sculpture captures the moment when Jesus, taken down from the cross, is given to his mother Mary.
 German Benedictine abbot and polymath Johannes Trithemius writes Steganographia, a major work on cryptography. The book is published in 1606. This book is in three volumes, and appears to be about magic — specifically, about using spirits to communicate over long distances. However, since the publication of a decryption key to the first two volumes in 1606, they were discovered to be actually concerned with cryptography and steganography. Until recently, the third volume was widely believed to be solely about magic, but the "magical" formulas have now been shown to be covertexts for yet more material on cryptography. The book was placed on the Index Librorum Prohibitorum in 1609 and removed in 1900.
German Benedictine abbot and polymath Johannes Trithemius writes Steganographia, a major work on cryptography. The book is published in 1606. This book is in three volumes, and appears to be about magic — specifically, about using spirits to communicate over long distances. However, since the publication of a decryption key to the first two volumes in 1606, they were discovered to be actually concerned with cryptography and steganography. Until recently, the third volume was widely believed to be solely about magic, but the "magical" formulas have now been shown to be covertexts for yet more material on cryptography. The book was placed on the Index Librorum Prohibitorum in 1609 and removed in 1900.
1499
(no entry for this year)
ESP Quick Facts
ESP Origins
In the early 1990's, Robert Robbins was a faculty member at Johns Hopkins, where he directed the informatics core of GDB — the human gene-mapping database of the international human genome project. To share papers with colleagues around the world, he set up a small paper-sharing section on his personal web page. This small project evolved into The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Support
In 1995, Robbins became the VP/IT of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, WA. Soon after arriving in Seattle, Robbins secured funding, through the ELSI component of the US Human Genome Project, to create the original ESP.ORG web site, with the formal goal of providing free, world-wide access to the literature of classical genetics.
ESP Rationale
Although the methods of molecular biology can seem almost magical to the uninitiated, the original techniques of classical genetics are readily appreciated by one and all: cross individuals that differ in some inherited trait, collect all of the progeny, score their attributes, and propose mechanisms to explain the patterns of inheritance observed.
ESP Goal
In reading the early works of classical genetics, one is drawn, almost inexorably, into ever more complex models, until molecular explanations begin to seem both necessary and natural. At that point, the tools for understanding genome research are at hand. Assisting readers reach this point was the original goal of The Electronic Scholarly Publishing Project.
ESP Usage
Usage of the site grew rapidly and has remained high. Faculty began to use the site for their assigned readings. Other on-line publishers, ranging from The New York Times to Nature referenced ESP materials in their own publications. Nobel laureates (e.g., Joshua Lederberg) regularly used the site and even wrote to suggest changes and improvements.
ESP Content
When the site began, no journals were making their early content available in digital format. As a result, ESP was obliged to digitize classic literature before it could be made available. For many important papers — such as Mendel's original paper or the first genetic map — ESP had to produce entirely new typeset versions of the works, if they were to be available in a high-quality format.
ESP Help
Early support from the DOE component of the Human Genome Project was critically important for getting the ESP project on a firm foundation. Since that funding ended (nearly 20 years ago), the project has been operated as a purely volunteer effort. Anyone wishing to assist in these efforts should send an email to Robbins.
ESP Plans
With the development of methods for adding typeset side notes to PDF files, the ESP project now plans to add annotated versions of some classical papers to its holdings. We also plan to add new reference and pedagogical material. We have already started providing regularly updated, comprehensive bibliographies to the ESP.ORG site.
ESP Picks from Around the Web (updated 06 MAR 2017 )
Old Science

Weird Science

Treating Disease with Fecal Transplantation
Fossils of miniature humans (hobbits) discovered in Indonesia

Dinosaur tail, complete with feathers, found preserved in amber.
Astronomy

Mysterious fast radio burst (FRB) detected in the distant universe.